Symptom finder - The causes of syncope
Symptom finder - The causes of syncope
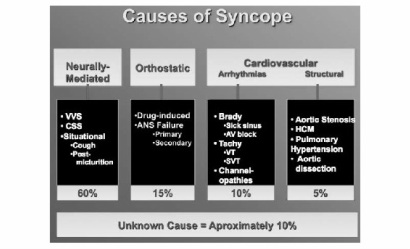
Syncope can be caused by neurological condition such as hysterical syncope or seizures, cardiovascular causes such as carotid sinus syndrome, cardia outflow obstruction, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, vasovagal syncope ( cough syncope, micturition syncope, situational syncope), arrhythmias ( stoke adam attack, sick sinus syndrome, ventricular tachycardia an supraventricular tachycardia) and orthostatic hypotension such as autonomic failure, hypovolemic, drug induced or prolonged bed rest.
What is syncope ? Syncope is transient loss of consciousness that occur due to impairment of cerebral blood flow.
Obstruction of cardiac outflow due to hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy or aortic stenosis will lead to an inability of cardiac output to increase with demand. This will later lead to syncope.
Syncope may be associated with hypoglycemia ( glucose level less than 2.5 mmol/l). Faintness or loss of consciousness may occur due to hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia commonly present after alcohol binge or on patient with diabetes who is treated with insulin.
Orthostatic hypotension or postural hypotension is a drop in the blood pressure while someone is standing. Orthostatic hypotension will lead to decrease in perfusion of the cerebrum which later lead to loss of consciousness. Medication such as opiates or hypertensive medication, hypovolemia and prolonged bed rest ( postural drop in blood pressure due to deconditioning of baroreceptor in the body) may lead to orthostatic hypotension. Pallor, low urine output and tachycardia are commonly associated with hypovolemia. Autonomic failure may occur with Guillain barre syndrome and diabetes mellitus.Autonomic failure may affect the ability of the body to maintain appropriate pressure.
Vasovagal syncope may cause syncope due to vagally mediation which slow the heart rates and peripheral vasolidation. Situation such as pain, prolonged standing,emotion and fear will make it worst. On examination, patient present with blurred vision, weakness, nausea and pallor and bradycardia. Situational syncope is due to vagal response excessive in nature due to offending stimuli.
Carotid sinus syndrome is due to hypersensitivity of the carotid sinus receptor which precipitate syncope and carotid sinus reflex by pressure from a tight collar or turning of the head. Palpitation may precede collapse in case arrhythmias.
Any paroxysmal discharges in the cortex or seizures may produce symptoms such as loss of consciousness,convulsion or behavioral symptoms. Collapse with sudden loss of muscle tone are due to atonic seizures. During a seizures patient may be incontinent and during post-ictal phase, the patient is drowsy and confused. Hysterical attack may appear normal during attack.
On examination, patient may appear clammy and pale. Pulse is taken during the attack of syncope as a way to elicit any arrhythmias. Vasovagal syncope usually present with bradycardia. Complete heart block may cause stoke adam attack which cause transient period of asystole. Alternating period of tachycardia and bradycardia are associated with sick sinus syndrome The differential diagnosis of rapid heart rates are ventricular, shock and supraventricular tachycardia. Syncope may happen in patient who suffer from carotid sinus syndrome due to pressure on carotid sinus which is located at the bifurcation of carotid arteries. Blood pressure is measured on supine and standing position to detect any postural drop.
Syncope can be caused by neurological condition such as hysterical syncope or seizures, cardiovascular causes such as carotid sinus syndrome, cardia outflow obstruction, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, vasovagal syncope ( cough syncope, micturition syncope, situational syncope), arrhythmias ( stoke adam attack, sick sinus syndrome, ventricular tachycardia an supraventricular tachycardia) and orthostatic hypotension such as autonomic failure, hypovolemic, drug induced or prolonged bed rest.
What is syncope ? Syncope is transient loss of consciousness that occur due to impairment of cerebral blood flow.
Obstruction of cardiac outflow due to hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy or aortic stenosis will lead to an inability of cardiac output to increase with demand. This will later lead to syncope.
Syncope may be associated with hypoglycemia ( glucose level less than 2.5 mmol/l). Faintness or loss of consciousness may occur due to hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia commonly present after alcohol binge or on patient with diabetes who is treated with insulin.
Orthostatic hypotension or postural hypotension is a drop in the blood pressure while someone is standing. Orthostatic hypotension will lead to decrease in perfusion of the cerebrum which later lead to loss of consciousness. Medication such as opiates or hypertensive medication, hypovolemia and prolonged bed rest ( postural drop in blood pressure due to deconditioning of baroreceptor in the body) may lead to orthostatic hypotension. Pallor, low urine output and tachycardia are commonly associated with hypovolemia. Autonomic failure may occur with Guillain barre syndrome and diabetes mellitus.Autonomic failure may affect the ability of the body to maintain appropriate pressure.
Vasovagal syncope may cause syncope due to vagally mediation which slow the heart rates and peripheral vasolidation. Situation such as pain, prolonged standing,emotion and fear will make it worst. On examination, patient present with blurred vision, weakness, nausea and pallor and bradycardia. Situational syncope is due to vagal response excessive in nature due to offending stimuli.
Carotid sinus syndrome is due to hypersensitivity of the carotid sinus receptor which precipitate syncope and carotid sinus reflex by pressure from a tight collar or turning of the head. Palpitation may precede collapse in case arrhythmias.
Any paroxysmal discharges in the cortex or seizures may produce symptoms such as loss of consciousness,convulsion or behavioral symptoms. Collapse with sudden loss of muscle tone are due to atonic seizures. During a seizures patient may be incontinent and during post-ictal phase, the patient is drowsy and confused. Hysterical attack may appear normal during attack.
On examination, patient may appear clammy and pale. Pulse is taken during the attack of syncope as a way to elicit any arrhythmias. Vasovagal syncope usually present with bradycardia. Complete heart block may cause stoke adam attack which cause transient period of asystole. Alternating period of tachycardia and bradycardia are associated with sick sinus syndrome The differential diagnosis of rapid heart rates are ventricular, shock and supraventricular tachycardia. Syncope may happen in patient who suffer from carotid sinus syndrome due to pressure on carotid sinus which is located at the bifurcation of carotid arteries. Blood pressure is measured on supine and standing position to detect any postural drop.
On auscultation, the present of ejection systolic murmur with soft second heart sound that radiates to carotid are the feature of aortic stenosis. Another diagnosis of ejection systolic murmur is hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. In this condition, the blood outflow is obstructed due to hypertrophy of the cardiac muscle.
The investigation may include full blood count, urea and electrolytes, blood glucose, BM stix, ECG,EEG, tilt table testing, V/Q scan and CT pulmonary angiography, echocardiography and 24 hour ECG.
In term of full blood count, raised white cell count is associated with peripheral vasolidation and septic shock. Reduction in hemoglobin level/anemia did occur due to hemorrhage which contributes to hypovolemia. Urea and electrolytes study are performed to rule out any electrolytes imbalance which lead to seizure. BM stix is a simple and rapid way of measuring blood glucose level, Blood glucose level /serum glucose level measurement however is more accurate than BM stix.
ECG is performed while the patient suffer from the acute attack to rule out any arrhythmias. Cardiac resuscitation should commence on cases o ventricular fibrillation due to pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Myocardial infarction is presented with ST elevation and Q wave.24 hour ECG is useful to document any episodes of arrhythmias. EEG is performed to detect any specific electrical changes in the cortex ( seizures). Tilt table testing is performed on patient with recurrent episodes of syncope. A 60 degree tilt will produce bradycardia, hypotension and syncope in vasovagal syncope patient within 30 minutes. Acute pulmonary emboli may be diagnosed with V/Q scan or CT pulmonary angiography. Echocardiography is useful to diagnose hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy and aortic stenosis.
The investigation may include full blood count, urea and electrolytes, blood glucose, BM stix, ECG,EEG, tilt table testing, V/Q scan and CT pulmonary angiography, echocardiography and 24 hour ECG.
In term of full blood count, raised white cell count is associated with peripheral vasolidation and septic shock. Reduction in hemoglobin level/anemia did occur due to hemorrhage which contributes to hypovolemia. Urea and electrolytes study are performed to rule out any electrolytes imbalance which lead to seizure. BM stix is a simple and rapid way of measuring blood glucose level, Blood glucose level /serum glucose level measurement however is more accurate than BM stix.
ECG is performed while the patient suffer from the acute attack to rule out any arrhythmias. Cardiac resuscitation should commence on cases o ventricular fibrillation due to pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Myocardial infarction is presented with ST elevation and Q wave.24 hour ECG is useful to document any episodes of arrhythmias. EEG is performed to detect any specific electrical changes in the cortex ( seizures). Tilt table testing is performed on patient with recurrent episodes of syncope. A 60 degree tilt will produce bradycardia, hypotension and syncope in vasovagal syncope patient within 30 minutes. Acute pulmonary emboli may be diagnosed with V/Q scan or CT pulmonary angiography. Echocardiography is useful to diagnose hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy and aortic stenosis.
