Pathology definition - DiGeorge Syndrome
DiGeorge Syndrome
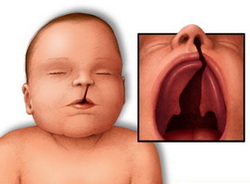
DiGeorge syndrome may present with increase susceptibility to recurrent fungal, protozoal and viral infection. Patient with DiGeorge syndrome may also present with cleft palate , congenital cardiovascular defect and tetany.
DiGeorge syndrome occurs due to failure in developing third and fourth pharyngeal pouch. There will be hypoplasia of the thyroid and parathyroid tissue. Hypocalcemia is common in case of parathyroid hypoplasia. T cell deficiency may occur due to hypoplasia of the thymus.
The treatment will aim to restore the immunity of the T cell by considering the transplant of the fetal thymus. DiGeorge syndrome is associated with microdeletion on the chromosome no 22.
DiGeorge syndrome may present with increase susceptibility to recurrent fungal, protozoal and viral infection. Patient with DiGeorge syndrome may also present with cleft palate , congenital cardiovascular defect and tetany.
DiGeorge syndrome occurs due to failure in developing third and fourth pharyngeal pouch. There will be hypoplasia of the thyroid and parathyroid tissue. Hypocalcemia is common in case of parathyroid hypoplasia. T cell deficiency may occur due to hypoplasia of the thymus.
The treatment will aim to restore the immunity of the T cell by considering the transplant of the fetal thymus. DiGeorge syndrome is associated with microdeletion on the chromosome no 22.
