|
|
Pathology definition - Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease
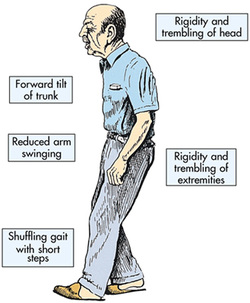
Parkinson disease may present with Parkinsonism. Parkinsonism may present with collective signs and symptoms such as bradykinesia, pill rolling tremor, shuffling gait, expressionless face, postural instability and rigidity.
The Parkinsonism symptoms/ Parkinson disease is treated with levodopa, dopamine agonists, amantidine, anti cholinergic and MAO- B inhibitors.
Besides Parkinson disease, there are a few more disorders which may cause Parkinsonism which include Shy Drager syndrome that is also accompany by autonomic dysregulation and orthostatic hypotension or drugs such as the intake os MPTP.
Parkinson disease may lead to loss of motor circuit of the basal ganglia stimulation due to loss of dopaminergic input to the striatum. There will also be the present of Lewy bodies in the substantia nigra neurons. Lewy bodies consist of intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies and eosinophil. There will be a pale region of the locus ceruleus and substantia nigra. There will be gliosis and loss of pigmented dopaminergic neurons in that area ( substantia nigra).
References
1.Hughes, A. J., S. E. Daniel, L. Kilford, and A. J. Lees. “Accuracy of Clinical Diagnosis of Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: A Clinico-Pathological Study of 100 Cases.” Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 55, no. 3 (March 1, 1992): 181–184. doi:10.1136/jnnp.55.3.181.
2.Hoehn, Margaret M., and Melvin D. Yahr. "Parkinsonism: onset, progression, and mortality." Neurology 50.2 (1998): 318-318.
Parkinson disease may present with Parkinsonism. Parkinsonism may present with collective signs and symptoms such as bradykinesia, pill rolling tremor, shuffling gait, expressionless face, postural instability and rigidity.
The Parkinsonism symptoms/ Parkinson disease is treated with levodopa, dopamine agonists, amantidine, anti cholinergic and MAO- B inhibitors.
Besides Parkinson disease, there are a few more disorders which may cause Parkinsonism which include Shy Drager syndrome that is also accompany by autonomic dysregulation and orthostatic hypotension or drugs such as the intake os MPTP.
Parkinson disease may lead to loss of motor circuit of the basal ganglia stimulation due to loss of dopaminergic input to the striatum. There will also be the present of Lewy bodies in the substantia nigra neurons. Lewy bodies consist of intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies and eosinophil. There will be a pale region of the locus ceruleus and substantia nigra. There will be gliosis and loss of pigmented dopaminergic neurons in that area ( substantia nigra).
References
1.Hughes, A. J., S. E. Daniel, L. Kilford, and A. J. Lees. “Accuracy of Clinical Diagnosis of Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease: A Clinico-Pathological Study of 100 Cases.” Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 55, no. 3 (March 1, 1992): 181–184. doi:10.1136/jnnp.55.3.181.
2.Hoehn, Margaret M., and Melvin D. Yahr. "Parkinsonism: onset, progression, and mortality." Neurology 50.2 (1998): 318-318.
