Pathology definition - Respiratory Acidosis
Respiratory Acidosis
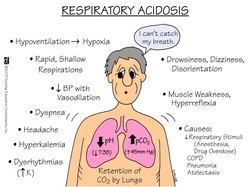
Respiratory acidosis is characterized by decreased in the pH but increased in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide( PCO2).
Increased in partial pressure of carbon dioxide may occur as a result of decreased in alveolar ventilation. This condition will lead to an increased in hydrogen bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) due to increased in hydrogen bicarbonate ion renal absorption that is stimulate by high partial pressure of carbon dioxide and low pH.
Respiratory acidosis may occur due to chronic obstructive lung disease, acute respiratory distress syndrome, kyphoscoliosis, narcotics, sedatives or opioid intakes, multiple sclerosis and polio.
Respiratory acidosis is treated by treating the underlying disorders. Respiratory acidosis may present with confusion, papilledema, asterixis, myoclonus, somnolence and hypoventilation.
Respiratory acidosis is characterized by decreased in the pH but increased in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide( PCO2).
Increased in partial pressure of carbon dioxide may occur as a result of decreased in alveolar ventilation. This condition will lead to an increased in hydrogen bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) due to increased in hydrogen bicarbonate ion renal absorption that is stimulate by high partial pressure of carbon dioxide and low pH.
Respiratory acidosis may occur due to chronic obstructive lung disease, acute respiratory distress syndrome, kyphoscoliosis, narcotics, sedatives or opioid intakes, multiple sclerosis and polio.
Respiratory acidosis is treated by treating the underlying disorders. Respiratory acidosis may present with confusion, papilledema, asterixis, myoclonus, somnolence and hypoventilation.
