Pathology definition - Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
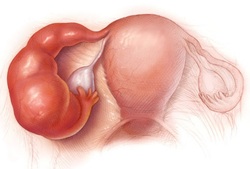
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease mostly affecting sexually active young nulliparous women with multiple sexual partner. Patient with pelvic inflammatory disease may complain of pyrexia, cervical purulent discharge, pain and tenderness in the motion of the cervix and lower abdominal pain.
Pelvic inflammatory disease may occur due to infection by chlamydia trachomatis, Trichomonas vaginalis and Neisseria gonorrhea. The effective treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease is antibiotics.
The infection may affect the fallopian tubes, ovaries and other structure around the pelvis. There will be edematous serosa of the fallopian tubes with covering by fibrin. Besides that there will be purulent exudate in the lumen as well as collection of pus which form pyosalpinx. The pus may also degraded into hydrosalpinx.
The common complication of pelvic inflammatory disease is periphepatitis or Fitz- Hugh - Curtis Syndrome that may present as right upper quadrant pain.
Pelvic inflammatory disease mostly affecting sexually active young nulliparous women with multiple sexual partner. Patient with pelvic inflammatory disease may complain of pyrexia, cervical purulent discharge, pain and tenderness in the motion of the cervix and lower abdominal pain.
Pelvic inflammatory disease may occur due to infection by chlamydia trachomatis, Trichomonas vaginalis and Neisseria gonorrhea. The effective treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease is antibiotics.
The infection may affect the fallopian tubes, ovaries and other structure around the pelvis. There will be edematous serosa of the fallopian tubes with covering by fibrin. Besides that there will be purulent exudate in the lumen as well as collection of pus which form pyosalpinx. The pus may also degraded into hydrosalpinx.
The common complication of pelvic inflammatory disease is periphepatitis or Fitz- Hugh - Curtis Syndrome that may present as right upper quadrant pain.
