Botulism symptoms
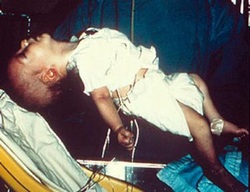
Botulism symptoms
What is botulism? Botulism is a syndrome that is associated with neurotoxins that are produced by Clostridium botulinum.These neurotoxin is known as the most toxic substance to man. There are five forms of botulism which are wound botulism, infant botulism, food borne botulism, inhalation botulism and adult botulism as well as intestinal colonization botulism. Symptoms typically develop 12 - 36 hours after the neurotoxins have been ingested.
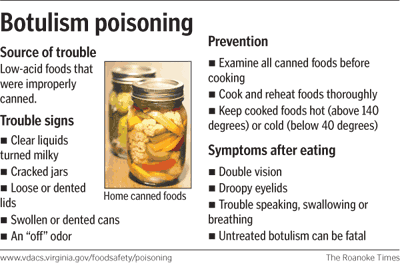
Botulism is a life threatening condition. However it is still rare. Botulism outbreak may occur due to contamination of the nome canned food or commercially canned food. Infants botulism is common mostly from food and wounds. The risk factors for botulism may include home made fermentation of food with home canning, iatrogenic case of botulism such as injection of unlicensed botulinum toxin A and honey ingestion by infant which predispose to colonization of the gastrointestinal tract and production of toxins. Patient more than 60 years old have higher fatality rate due to botulism. Intravenous drig users are also predispose to wound botulism.
The general prevention include careful steps are taken while canning low acidic food such as betts, beans,asparagus and corns. It is vital to boil home canned food for 10 minutes prior to eating. Avoid intake of food which is stored in bulging cans and stop giving honey to 1 years old infants. Thorough but rapid screening of suspected case should be performed to prevent possible outbreak.
What is Clostridium botulinum ? Clostridium botulinum is a group of anaerobe gram positive rods which produce patent neurotoxins and spores. The type of organism is ranged from type A to type G based on the nature of the neurotoxin and antibodies produced. Human disease is associated with toxin from types A, B, E and F of Clostridium botulinum. Type A Clostridium botulinum is found mostly in the China and Western USA. Type B is found in the Europe and Eastern US while type F is often associated with fish product and can be found in Alaska and worldwide. Spores from Clostridium botulinum are found in marine sediment and soil. These spores can be destroyed at the temperature of 120 degree celsius .
Botulism is diagnosed when someone is presenting with bilateral descending weakness, bilateral cranial neuropathies,no sensory abnormalities, no fever and remain alert and awake as the syndrome progress.
Laboratory studies may include identification fo the toxin from the food, stools of serum sample. In patient with wound botulism, the mouse bioassay sensitivity has been determined to be 68% .
Differential diagnosis of botulism are heavy metal intoxication , poliomyelitis, stroke, Miller Fsiher variant of Guillain Barre syndrome, tick paralysis, Eaton- Lambert syndrome and myasthenia gravis.
The treatment may include supportive care, antitoxin ( toxin types A, B, and E), antibiotic ( especially for wound botulism ) and BIG - IV or intravenous human botulism immunoglobulin which is useful in infant and administer early in the course of the disease. Long term rehabilitation is often required. Difficulty breathing, dizziness, weakness and fatigue are commonly present in patient who just recover from botulism.
What is botulism? Botulism is a syndrome that is associated with neurotoxins that are produced by Clostridium botulinum.These neurotoxin is known as the most toxic substance to man. There are five forms of botulism which are wound botulism, infant botulism, food borne botulism, inhalation botulism and adult botulism as well as intestinal colonization botulism. Symptoms typically develop 12 - 36 hours after the neurotoxins have been ingested.
Botulism is a life threatening condition. However it is still rare. Botulism outbreak may occur due to contamination of the nome canned food or commercially canned food. Infants botulism is common mostly from food and wounds. The risk factors for botulism may include home made fermentation of food with home canning, iatrogenic case of botulism such as injection of unlicensed botulinum toxin A and honey ingestion by infant which predispose to colonization of the gastrointestinal tract and production of toxins. Patient more than 60 years old have higher fatality rate due to botulism. Intravenous drig users are also predispose to wound botulism.
The general prevention include careful steps are taken while canning low acidic food such as betts, beans,asparagus and corns. It is vital to boil home canned food for 10 minutes prior to eating. Avoid intake of food which is stored in bulging cans and stop giving honey to 1 years old infants. Thorough but rapid screening of suspected case should be performed to prevent possible outbreak.
What is Clostridium botulinum ? Clostridium botulinum is a group of anaerobe gram positive rods which produce patent neurotoxins and spores. The type of organism is ranged from type A to type G based on the nature of the neurotoxin and antibodies produced. Human disease is associated with toxin from types A, B, E and F of Clostridium botulinum. Type A Clostridium botulinum is found mostly in the China and Western USA. Type B is found in the Europe and Eastern US while type F is often associated with fish product and can be found in Alaska and worldwide. Spores from Clostridium botulinum are found in marine sediment and soil. These spores can be destroyed at the temperature of 120 degree celsius .
Botulism is diagnosed when someone is presenting with bilateral descending weakness, bilateral cranial neuropathies,no sensory abnormalities, no fever and remain alert and awake as the syndrome progress.
Laboratory studies may include identification fo the toxin from the food, stools of serum sample. In patient with wound botulism, the mouse bioassay sensitivity has been determined to be 68% .
Differential diagnosis of botulism are heavy metal intoxication , poliomyelitis, stroke, Miller Fsiher variant of Guillain Barre syndrome, tick paralysis, Eaton- Lambert syndrome and myasthenia gravis.
The treatment may include supportive care, antitoxin ( toxin types A, B, and E), antibiotic ( especially for wound botulism ) and BIG - IV or intravenous human botulism immunoglobulin which is useful in infant and administer early in the course of the disease. Long term rehabilitation is often required. Difficulty breathing, dizziness, weakness and fatigue are commonly present in patient who just recover from botulism.