Pathology definition - Leiomyoma
Leiomyoma
Leiomyoma is also known as uterine fibroids. Leiomyoma may present with acute or sometimes recurrent pain in the pelvic, frequent period of menstruation and profuse menstruation.This will be justified by iron deficiency anemia.There will be decompression of the bladder which lead to urinary frequency and the common complication is infertility.
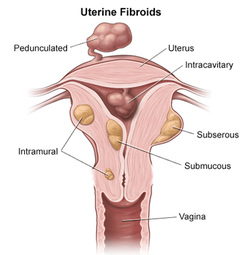
Leiomyoma may present with large, multiple irregular heterogenous tumor in the myometrium. Which is intramural form of leiomyoma. Leiomyoma may also present beneath the serosa ( subserosal leiomyoma) and beneath the endometrium ( submucosal leiomyoma). There will be giant cells and cellular atypia as well as whorled pattern of the smooth muscle bundles.
Leiomyoma is the common benign tumor of the female genitalia tract. Leiomyoma commonly affect women in reproductive age. The treatment of leiomyoma may focus on myomectomy or hysterectomy. Leiomyoma may not develop into leiomyosarcomas. Leiomyosarcomas arise de novo with area of hemorrhage and necrosis in the cervix.
Leiomyoma is also known as uterine fibroids. Leiomyoma may present with acute or sometimes recurrent pain in the pelvic, frequent period of menstruation and profuse menstruation.This will be justified by iron deficiency anemia.There will be decompression of the bladder which lead to urinary frequency and the common complication is infertility.
Leiomyoma may present with large, multiple irregular heterogenous tumor in the myometrium. Which is intramural form of leiomyoma. Leiomyoma may also present beneath the serosa ( subserosal leiomyoma) and beneath the endometrium ( submucosal leiomyoma). There will be giant cells and cellular atypia as well as whorled pattern of the smooth muscle bundles.
Leiomyoma is the common benign tumor of the female genitalia tract. Leiomyoma commonly affect women in reproductive age. The treatment of leiomyoma may focus on myomectomy or hysterectomy. Leiomyoma may not develop into leiomyosarcomas. Leiomyosarcomas arise de novo with area of hemorrhage and necrosis in the cervix.
