Pediatric Definition - Celiac Disease
Celiac Disease
The differential diagnosis of celiac disease may include food allergies, Crohn’s disease, Zollinger - Ellison Syndrome and immunodeficiency associated with diarrhea.
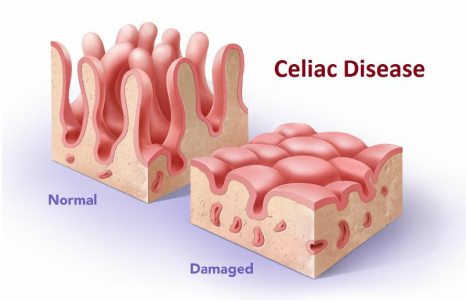
Celiac disease is common on 6 to 24 months of age. Celiac disease can be detected with duodenal biopsy and the present of IgA anti endomysial Antibody, transglutaminase antibody and anemia. Celiac disease is a form of immune mediated enteropathy.
Celiac disease is associated with IgA deficiency, autoimmune thyroiditis, trisomy 21, type 1 diabetes and turner syndrome.
The characteristic of celiac disease are vomiting, abdominal pain, abdominal distention, constipation, diarrhea, failure to thrive, edema, pruritic rash, arthritis, irritability and fatty stools.
The complications of celiac disease are infertility, osteopenia and T cell lymphoma enteropathy.
Patient with celiac disease is treated with gluten free diet ( wheat, rye and barley) as well as corticosteroids.
The differential diagnosis of celiac disease may include food allergies, Crohn’s disease, Zollinger - Ellison Syndrome and immunodeficiency associated with diarrhea.
Celiac disease is common on 6 to 24 months of age. Celiac disease can be detected with duodenal biopsy and the present of IgA anti endomysial Antibody, transglutaminase antibody and anemia. Celiac disease is a form of immune mediated enteropathy.
Celiac disease is associated with IgA deficiency, autoimmune thyroiditis, trisomy 21, type 1 diabetes and turner syndrome.
The characteristic of celiac disease are vomiting, abdominal pain, abdominal distention, constipation, diarrhea, failure to thrive, edema, pruritic rash, arthritis, irritability and fatty stools.
The complications of celiac disease are infertility, osteopenia and T cell lymphoma enteropathy.
Patient with celiac disease is treated with gluten free diet ( wheat, rye and barley) as well as corticosteroids.