Leptospirosis symptom

Leptospirosis symptoms
What is leptospirosis? Leptospirosis is a zoonotic type of infection which is caused by leptospire pathogen.
Most leptospirosis infection are undetectable/ asymptomatic. Leptospirosis is the common infection worldwide with an incidence higher than usual.
Worldwide leptospirosis remains as an undiagnosed caused of aseptic meningitis and encephalitis. Leptospirosis is most commonly affecting the male due to preference of recreational activities and occupation. 10% of cases of encephalitis and meningitis are associated with the serological evidence of leptospirosis.
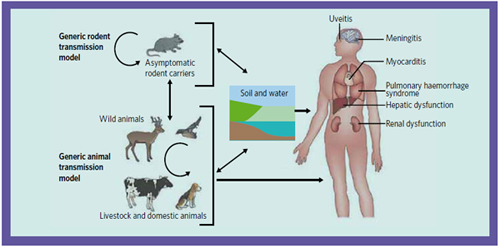
The most common cause of leptospirosis in the US are infection by l. interrogans serovar icterhaemorrhagiae ( rats), pomona, bratislava, australis, autumnalis ( cattle and swine), canicola ( dog) and hebdominis.
The most common cause of leptospirosis in the UK is due to the close contact between individuals and livestocks which are infected by l. interrogans serovar hardjo.
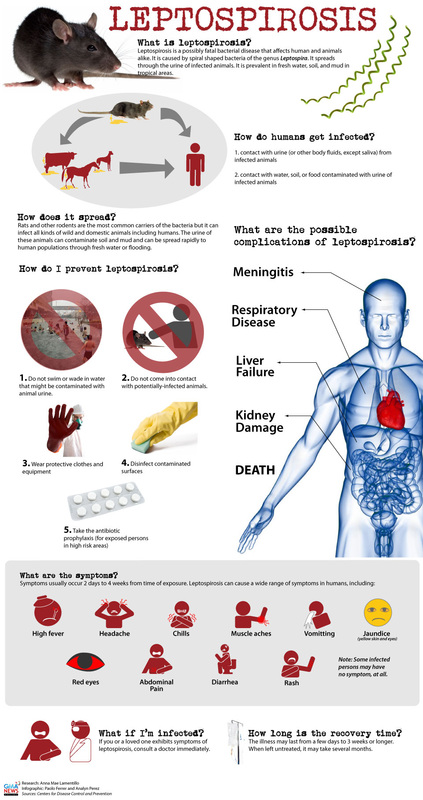
The risk factors for developing leptospirosis includes the close contact of the abraded /wounded mucous membrane or skin with vegetation, water or soil that is contaminated with infected animals or urine. Drink and food consumption may also contribute to leptospirosis.( as a mode of transmissions).
Certain types of occupation may predispose the patient to leptospirosis infection such as campers, bathers, sewer workers,abattoir workers, miners, farmers, triathlon participants and strawberry harvesters. Disaster such as flooding or living in an urban slum area may also predispose the patient to leptospirosis.
Leptospirosis can be prevented by administrating 200 mg doxycycline in military personnel and travelers who are exposed to leptospira.
Workers are advised to wear protective clothes, gloves and boots if the job expose them to leptospira. The incidence of human leptospirosis may also decrease by controlling the population of the rodents.
Initially, leptospira will bind to the skin through elastin. This is facilitated with the present of transmembrane protein OmpL37. After binding to the endothelial surface, leptospira will disturb the barrier of the endothelilai and cause the dissemination of leptospira in various organs and tissues of the patient. Hemorrhage may also occured due to the direct effect of the leptospira on the endothelium.
Leptospirosis is caused by a microorganism called leptospira interrogans which is further classified into 200 or more serovars. Leptospirosis has been found to be caused by 24 sero groups of L. interrogans, The resevoirs for leptospirosis are the domestic and wild animals. The main resevoir for L.interrogans serovar icterohaemorrhagiae are the rats. 1-2 weeks or 2- 25 days are the incubation period between infection and development of the symptoms.
While taking the history, it is important to keep a high index of suspicion. The history should focus on work or leisure activities which predispose to exposure to leptospirosis. Leptospirosis may mimic other vital disease based on its protean manifestation.
There are 2 forms of leptospirosis ehich could be differentiated based on the physical finding. Weil’s syndrome or icteric leptospirosis is characterized by renal failure and jaundice which are the most severe complication of this disease as well as certain features of anicteric leptospirosis described below. Anicteric leptospirosis is presented with neck stiffness, conjunctival suffusion, calf muscle myalgia, biphasic fever and chills, palatal enanthem ( rash) which is hemorrhagic sometimes, headache, confusion, changes in behavior and depression ( central nervous system) and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Laboratory investigation may include full blood count, urea and electrolyte, CSF, urine culture and blood culture. Dark field microscope may reveal the present of leptospira organism in the blood , CSF or urine of the infected patients. Leptospira may be absent from the CSF or blood after 2- 3 days but leptospira tend to stay in the kidney. Thrombocytopenia may occur and abnormal renal function test is confirmed. An increase in bilirubin ( abnormal liver function test) indicates the severity of the illness. There is also an increase in creatinophosphokinase level. Urine culture is positive when taken during the first week while CSF and blood culture are positive after the first week up to the 4th weeks. All leptospirosis culture requires prolonged period of incubation ( 4 months ) and special media.
Serological test is used as the main diagnostic test in diagnosing leptospirosis. The most prefer serological test for diagnosis is known as microscopic agglutination test. The useful criteria for diagnosing leptospirosis is a transition from seronegative to 1: 100 or fourfold increase. Other valuable diagnostic test is the present of IgM antibodies against the leptospira. The downfall of this test is based on the concept that IgM antibodies may present for a long time after acute leptospirosis infection. ( 1 or 2 years).
Other tests include pulsed field gel electrophoresis to detect various leptospira serovars or polymerase chain reaction to detect the DNA of leptospira spp.
Imaging technique such as X ray or CT scan is only considered if respiratory symptoms are dominant. Lumbar puncture is useful. Pathological finding may include the present of leptospira organism in tissue biopsy specimen.
Leptospirosis should always be considered in patient who is febrile and at risk of infection due to recreational activities or occupations. Leptospirosis is often misdiagnosed as infection which is viral in origin such as influenza. Other differential diagnosis are Rickettsioses, hemolytic uremic syndrome, acute meningitis, Hantavirus fever ( Crimean - Congo ) or viral hemorrhagic fever and traveler who suffer from fever while returning from traveling.
The treatment of leptospirosis initially is smaller dose of penicillin ( 4- 10 millions units of penicillin G intravenously daily as considered ). 1g Ceftriaxone intravenously daily is also considered. The duration of treatment is 7 days. Others antimicrobial agents are also considered such as 100 mg orally doxycycline every 12 hours for 7 days for leptospirosis which is mild in nature or another alternative such as azithromycin. In case of the patient developing acute renal failure, nephrologist’s opinion should be considered. In severe case of leptospirosis , steroid has been considered especially if the renal system or pulmonary systems are afflicted. Patient who is thrombocytopenic, jaundice and suffer from acute renal failure should be refer for admission. Improvement in term of laboratory and clinical response may permit discharge of the patient.
Patient with severe leptospirosis will require a follow up visit, a week after medication has been stopped. Patient with mild leptospirosis require no follow up. It is improtant to discuss with the patient who profession predispose them to leptospirosis about wearing significant protective clothing.
Mortality is 50% in untreated cases of sever leptospirosis. The mortality rate is 50% in untreated cases of severe leptospirosis. The mortality rate is 20% for cases of severe leptospirosis with kidney and liver failure That is treated with appropriate antibiotics.
The main cause of death are vascular dysfunction with bleeding severe in nature , myocarditis that lead to arrhythmias, adult respiratory distress syndrome and hepatorenal syndrome.
The patient may also develops a Jarisch Herxheimer reaction while on treatment, Several months are required for recovery in untreated cases. Jaundice and severe leptospirosis is known Weil’s syndrome. Fort Bragg fever is a leptospirosis syndrome with pretibial rash and fever. In pregnant woman , abortion is ensure if leptospirosis occur in the first month of pregnancy. Congenital infection is rare.
What is leptospirosis? Leptospirosis is a zoonotic type of infection which is caused by leptospire pathogen.
Most leptospirosis infection are undetectable/ asymptomatic. Leptospirosis is the common infection worldwide with an incidence higher than usual.
Worldwide leptospirosis remains as an undiagnosed caused of aseptic meningitis and encephalitis. Leptospirosis is most commonly affecting the male due to preference of recreational activities and occupation. 10% of cases of encephalitis and meningitis are associated with the serological evidence of leptospirosis.
The most common cause of leptospirosis in the US are infection by l. interrogans serovar icterhaemorrhagiae ( rats), pomona, bratislava, australis, autumnalis ( cattle and swine), canicola ( dog) and hebdominis.
The most common cause of leptospirosis in the UK is due to the close contact between individuals and livestocks which are infected by l. interrogans serovar hardjo.
The risk factors for developing leptospirosis includes the close contact of the abraded /wounded mucous membrane or skin with vegetation, water or soil that is contaminated with infected animals or urine. Drink and food consumption may also contribute to leptospirosis.( as a mode of transmissions).
Certain types of occupation may predispose the patient to leptospirosis infection such as campers, bathers, sewer workers,abattoir workers, miners, farmers, triathlon participants and strawberry harvesters. Disaster such as flooding or living in an urban slum area may also predispose the patient to leptospirosis.
Leptospirosis can be prevented by administrating 200 mg doxycycline in military personnel and travelers who are exposed to leptospira.
Workers are advised to wear protective clothes, gloves and boots if the job expose them to leptospira. The incidence of human leptospirosis may also decrease by controlling the population of the rodents.
Initially, leptospira will bind to the skin through elastin. This is facilitated with the present of transmembrane protein OmpL37. After binding to the endothelial surface, leptospira will disturb the barrier of the endothelilai and cause the dissemination of leptospira in various organs and tissues of the patient. Hemorrhage may also occured due to the direct effect of the leptospira on the endothelium.
Leptospirosis is caused by a microorganism called leptospira interrogans which is further classified into 200 or more serovars. Leptospirosis has been found to be caused by 24 sero groups of L. interrogans, The resevoirs for leptospirosis are the domestic and wild animals. The main resevoir for L.interrogans serovar icterohaemorrhagiae are the rats. 1-2 weeks or 2- 25 days are the incubation period between infection and development of the symptoms.
While taking the history, it is important to keep a high index of suspicion. The history should focus on work or leisure activities which predispose to exposure to leptospirosis. Leptospirosis may mimic other vital disease based on its protean manifestation.
There are 2 forms of leptospirosis ehich could be differentiated based on the physical finding. Weil’s syndrome or icteric leptospirosis is characterized by renal failure and jaundice which are the most severe complication of this disease as well as certain features of anicteric leptospirosis described below. Anicteric leptospirosis is presented with neck stiffness, conjunctival suffusion, calf muscle myalgia, biphasic fever and chills, palatal enanthem ( rash) which is hemorrhagic sometimes, headache, confusion, changes in behavior and depression ( central nervous system) and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Laboratory investigation may include full blood count, urea and electrolyte, CSF, urine culture and blood culture. Dark field microscope may reveal the present of leptospira organism in the blood , CSF or urine of the infected patients. Leptospira may be absent from the CSF or blood after 2- 3 days but leptospira tend to stay in the kidney. Thrombocytopenia may occur and abnormal renal function test is confirmed. An increase in bilirubin ( abnormal liver function test) indicates the severity of the illness. There is also an increase in creatinophosphokinase level. Urine culture is positive when taken during the first week while CSF and blood culture are positive after the first week up to the 4th weeks. All leptospirosis culture requires prolonged period of incubation ( 4 months ) and special media.
Serological test is used as the main diagnostic test in diagnosing leptospirosis. The most prefer serological test for diagnosis is known as microscopic agglutination test. The useful criteria for diagnosing leptospirosis is a transition from seronegative to 1: 100 or fourfold increase. Other valuable diagnostic test is the present of IgM antibodies against the leptospira. The downfall of this test is based on the concept that IgM antibodies may present for a long time after acute leptospirosis infection. ( 1 or 2 years).
Other tests include pulsed field gel electrophoresis to detect various leptospira serovars or polymerase chain reaction to detect the DNA of leptospira spp.
Imaging technique such as X ray or CT scan is only considered if respiratory symptoms are dominant. Lumbar puncture is useful. Pathological finding may include the present of leptospira organism in tissue biopsy specimen.
Leptospirosis should always be considered in patient who is febrile and at risk of infection due to recreational activities or occupations. Leptospirosis is often misdiagnosed as infection which is viral in origin such as influenza. Other differential diagnosis are Rickettsioses, hemolytic uremic syndrome, acute meningitis, Hantavirus fever ( Crimean - Congo ) or viral hemorrhagic fever and traveler who suffer from fever while returning from traveling.
The treatment of leptospirosis initially is smaller dose of penicillin ( 4- 10 millions units of penicillin G intravenously daily as considered ). 1g Ceftriaxone intravenously daily is also considered. The duration of treatment is 7 days. Others antimicrobial agents are also considered such as 100 mg orally doxycycline every 12 hours for 7 days for leptospirosis which is mild in nature or another alternative such as azithromycin. In case of the patient developing acute renal failure, nephrologist’s opinion should be considered. In severe case of leptospirosis , steroid has been considered especially if the renal system or pulmonary systems are afflicted. Patient who is thrombocytopenic, jaundice and suffer from acute renal failure should be refer for admission. Improvement in term of laboratory and clinical response may permit discharge of the patient.
Patient with severe leptospirosis will require a follow up visit, a week after medication has been stopped. Patient with mild leptospirosis require no follow up. It is improtant to discuss with the patient who profession predispose them to leptospirosis about wearing significant protective clothing.
Mortality is 50% in untreated cases of sever leptospirosis. The mortality rate is 50% in untreated cases of severe leptospirosis. The mortality rate is 20% for cases of severe leptospirosis with kidney and liver failure That is treated with appropriate antibiotics.
The main cause of death are vascular dysfunction with bleeding severe in nature , myocarditis that lead to arrhythmias, adult respiratory distress syndrome and hepatorenal syndrome.
The patient may also develops a Jarisch Herxheimer reaction while on treatment, Several months are required for recovery in untreated cases. Jaundice and severe leptospirosis is known Weil’s syndrome. Fort Bragg fever is a leptospirosis syndrome with pretibial rash and fever. In pregnant woman , abortion is ensure if leptospirosis occur in the first month of pregnancy. Congenital infection is rare.