Pathology definition - Lupus Nephropathy
Lupus nephropathy
Lupus nephropathy is a renal manifestation of SLE ( systemic lupus erythematous). Lupus nephropathy is divided based on the renal histological forms.
Type 1 lupus nephropathy presents with normal renal histological patterns. There will be no clinical symptoms and signs. No treatment is required if the patient suffer from type 1 lupus nephropathy.
Type II lupus nephropathy present with segmental and focal glomerular involvement with increase in the matrix of mesangium. Patient with type II lupus nephropathy may present with proteinuria and hematuria. No treatment is required for type II lupus nephropathy. Type III lupus neprhopathy may present with extensive damage to the glomeruli. However it involve only half of the glomeruli. Type III lupus nephropathy is also known as proliferative forms of lupus nephropathy. The treatment of type III lupus nephropathy includes immunosuppressive therapy such as corticosteroid, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine.
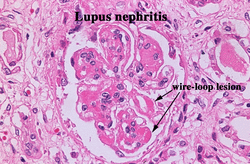
Type IV lupus nephropathy is also known as diffuse proliferative forms. There will be proliferation of endothelial cells and thickening of the glomerular basement membrane. There will be subendothelial deposition of the immune complex which is characterized by wire loop abnormality. There will also be scarring, proliferation of mesangial and marked inflammation which involves the whole glomeruli ( severe reaction). Type IV lupus nephropathy may present with combination of nephrotic syndrome and nephritic syndrome. The treatment of type IV lupus nephropathy includes immunosuppressive therapy such as corticosteroid, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine.
Type V lupus nephropathy may present with similar characteristic as membranous glomerulonephritis. Type V lupus nephropathy is known as membranous form of lupus nephropathy. Type V lupus nephropathy is treated with immunosuppressive therapy such as corticosteroid, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine.
Lupus nephropathy is a renal manifestation of SLE ( systemic lupus erythematous). Lupus nephropathy is divided based on the renal histological forms.
Type 1 lupus nephropathy presents with normal renal histological patterns. There will be no clinical symptoms and signs. No treatment is required if the patient suffer from type 1 lupus nephropathy.
Type II lupus nephropathy present with segmental and focal glomerular involvement with increase in the matrix of mesangium. Patient with type II lupus nephropathy may present with proteinuria and hematuria. No treatment is required for type II lupus nephropathy. Type III lupus neprhopathy may present with extensive damage to the glomeruli. However it involve only half of the glomeruli. Type III lupus nephropathy is also known as proliferative forms of lupus nephropathy. The treatment of type III lupus nephropathy includes immunosuppressive therapy such as corticosteroid, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine.
Type IV lupus nephropathy is also known as diffuse proliferative forms. There will be proliferation of endothelial cells and thickening of the glomerular basement membrane. There will be subendothelial deposition of the immune complex which is characterized by wire loop abnormality. There will also be scarring, proliferation of mesangial and marked inflammation which involves the whole glomeruli ( severe reaction). Type IV lupus nephropathy may present with combination of nephrotic syndrome and nephritic syndrome. The treatment of type IV lupus nephropathy includes immunosuppressive therapy such as corticosteroid, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine.
Type V lupus nephropathy may present with similar characteristic as membranous glomerulonephritis. Type V lupus nephropathy is known as membranous form of lupus nephropathy. Type V lupus nephropathy is treated with immunosuppressive therapy such as corticosteroid, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine.
