Pediatric Definition - Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis
Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis
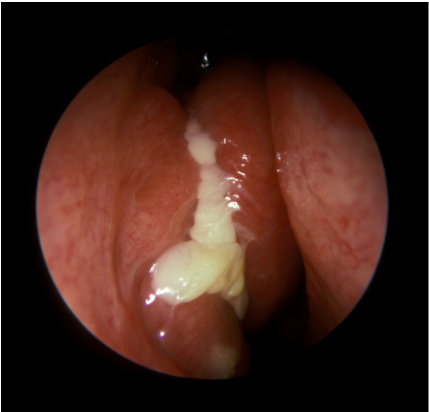
The common symptoms and signs of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis are headache, fever, facial pain, nasal drainage, nasal congestion and postnasal drainage.
Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis may carry complication such as orbital cellulitis, preseptal cellulitis, osteitis of frontal bone ( Pott’s puffy tumor), cavernous sinus thrombosis, epidural abscess, subdural abscess, meningitis and brain abscess.
The differential diagnosis of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis is acute viral rhinitis.
The treatment may be initiated if the children is not improving for 10 to 14 days or with worsening of symptoms such as purulent nasal discharge or 3 - 4 days fever more than 39 degree celsius.
The first line of treatment is antibiotic amoxicillin or amoxicillin clavulanate. Cefuroxime or cefdinir is only considered for non type 1 hypersensitivity to penicillin.
The common symptoms and signs of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis are headache, fever, facial pain, nasal drainage, nasal congestion and postnasal drainage.
Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis may carry complication such as orbital cellulitis, preseptal cellulitis, osteitis of frontal bone ( Pott’s puffy tumor), cavernous sinus thrombosis, epidural abscess, subdural abscess, meningitis and brain abscess.
The differential diagnosis of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis is acute viral rhinitis.
The treatment may be initiated if the children is not improving for 10 to 14 days or with worsening of symptoms such as purulent nasal discharge or 3 - 4 days fever more than 39 degree celsius.
The first line of treatment is antibiotic amoxicillin or amoxicillin clavulanate. Cefuroxime or cefdinir is only considered for non type 1 hypersensitivity to penicillin.