|
|
Pathology definition - Celiac disease
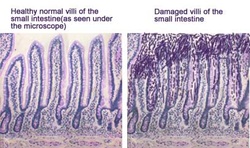 Damaged villi of the small intestine is indication of celiac disease
Damaged villi of the small intestine is indication of celiac disease
Celiac disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune mediated disorder due to intolerance to the gluten containing product such as barley, wheat, oat and rye). There will be an infiltration of the plasma cells and lymphocytes in the lamina propria. There will be an trophy of the villi of the small intestine and loss of brush border.
Celiac disease is associated with HLA- DR3 and HLA - DQw2. Celiac disease may present with detection of antiendomyseal antibody and anitigliadin antibodies as well as abnormality of the D xylose test. Patient may also develop enteropathy type T - cell lymphoma.
Patient who suffer from celiac disease may present with failure to thrive or growth retardation. Patient may also complain of itchiness on the extensor surface of the extremities or on the neck, trunk or scalp. This is known as dermatitis herpetiformis.
Clinically dermatitis herpetiformis is symmetrical, recurrent, subepidermal blister. Dermatitis herpetiformis is commonly treated with dapsone.
The treatment will focus on restriction and considering gluten free diet.
Celiac disease commonly affecting people in the northern europe. However another condition tropical sprue which present with almost similar symptoms and signs are commonly affecting people in the tropical area. Tropical sprue is more infectious in origin with overgrowth of the enterotoxigenic organism which lead to malabsorption syndrome and treated with antibiotic.
References
1.Green, Peter H.R., and Christophe Cellier. “Celiac Disease.” New England Journal of Medicine 357, no. 17 (2007): 1731–1743. doi:10.1056/NEJMra071600.
2.Schuppan, Detlef, Yvonne Junker, and Donatella Barisani. “Celiac Disease: From Pathogenesis to Novel Therapies.” Gastroenterology 137, no. 6 (December 2009): 1912–1933. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.008.
Celiac disease is an autoimmune mediated disorder due to intolerance to the gluten containing product such as barley, wheat, oat and rye). There will be an infiltration of the plasma cells and lymphocytes in the lamina propria. There will be an trophy of the villi of the small intestine and loss of brush border.
Celiac disease is associated with HLA- DR3 and HLA - DQw2. Celiac disease may present with detection of antiendomyseal antibody and anitigliadin antibodies as well as abnormality of the D xylose test. Patient may also develop enteropathy type T - cell lymphoma.
Patient who suffer from celiac disease may present with failure to thrive or growth retardation. Patient may also complain of itchiness on the extensor surface of the extremities or on the neck, trunk or scalp. This is known as dermatitis herpetiformis.
Clinically dermatitis herpetiformis is symmetrical, recurrent, subepidermal blister. Dermatitis herpetiformis is commonly treated with dapsone.
The treatment will focus on restriction and considering gluten free diet.
Celiac disease commonly affecting people in the northern europe. However another condition tropical sprue which present with almost similar symptoms and signs are commonly affecting people in the tropical area. Tropical sprue is more infectious in origin with overgrowth of the enterotoxigenic organism which lead to malabsorption syndrome and treated with antibiotic.
References
1.Green, Peter H.R., and Christophe Cellier. “Celiac Disease.” New England Journal of Medicine 357, no. 17 (2007): 1731–1743. doi:10.1056/NEJMra071600.
2.Schuppan, Detlef, Yvonne Junker, and Donatella Barisani. “Celiac Disease: From Pathogenesis to Novel Therapies.” Gastroenterology 137, no. 6 (December 2009): 1912–1933. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.008.
