|
|
Pathology definition - Subdural hematoma
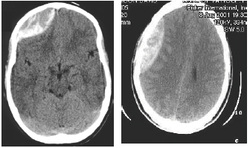
Subdural hematoma
Subdural hematoma may present with signs and symptoms such as headache and alteration of the mental and conscious level.
Subdural hematoma may present due to tearing of the bridging veins between the cerebrum and venous sinuses in the dura. Patient may develop clinical signs gradually usually hours to weeks after injury. The common causes of subdural hematoma is injury to the head.
Subdural hematoma is characterized by the collection of blood between the arachnoid and dura. The hematoma may grow due to the action of osmotic movement of the water. Bleeding from subdural hematoma usually self limiting. However, chronic subdural hematoma may develop with the formation of granulation tissue.
Crescent shaped disk which crosses the lines of suture is a trademark of subdural hematoma which is detected by CT scan of the head. The main treatment of subdural hematoma is surgical drainage of the blood.
References
1.Stone, James L., Mohamad H. S. Rifai, Oscar Sugar, Robert G. R. Lang, John B. Oldershaw, and Robert A. Moody. “Subdural Hematomas: I. Acute Subdural Hematoma: Progress in Definition, Clinical Pathology, and Therapy.” Surgical Neurology 19, no. 3 (March 1983): 216–231. doi:10.1016/S0090-3019(83)80005-6.
2.Thomas-Marc Markwalder. “Chronic Subdural Hematomas: A Review.” Research-article. May 8, 2009.
Subdural hematoma may present with signs and symptoms such as headache and alteration of the mental and conscious level.
Subdural hematoma may present due to tearing of the bridging veins between the cerebrum and venous sinuses in the dura. Patient may develop clinical signs gradually usually hours to weeks after injury. The common causes of subdural hematoma is injury to the head.
Subdural hematoma is characterized by the collection of blood between the arachnoid and dura. The hematoma may grow due to the action of osmotic movement of the water. Bleeding from subdural hematoma usually self limiting. However, chronic subdural hematoma may develop with the formation of granulation tissue.
Crescent shaped disk which crosses the lines of suture is a trademark of subdural hematoma which is detected by CT scan of the head. The main treatment of subdural hematoma is surgical drainage of the blood.
References
1.Stone, James L., Mohamad H. S. Rifai, Oscar Sugar, Robert G. R. Lang, John B. Oldershaw, and Robert A. Moody. “Subdural Hematomas: I. Acute Subdural Hematoma: Progress in Definition, Clinical Pathology, and Therapy.” Surgical Neurology 19, no. 3 (March 1983): 216–231. doi:10.1016/S0090-3019(83)80005-6.
2.Thomas-Marc Markwalder. “Chronic Subdural Hematomas: A Review.” Research-article. May 8, 2009.
