Pathology definition - Sarcoidosis
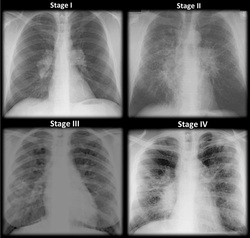 Different stages of sarcoidosis
Different stages of sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
May present with symptoms and signs such as erythema nodosum, shortness of breath, malaise, poly arthritis, hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, enlargement of the liver and spleen ( hepatosplenomegaly) and fever.
Sarcoidosis may affect organs such as eyes, skin, lymph nodes, spleen, lung, liver, salivary gland and bone marrow.
Sarcoidosis is common in African american women and west european women age 20 - 40 years old. Laboratory investigations may reveal increase in ACE level, ESR and decreased in the total lung capacity, reduced sensitivity to antigens skin test and hypergammaglobulinemia. Chest x ray may reveal infiltration of the interstitium and bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy.
Sarcoidosis may present with non caseating granuloma. There is a fibrotic center with Langhan giant cells and epithelioid cells. Schaumann bodies and asteroid bodies may also present.
The treatment of sarcoidosis may include corticosteroids.
May present with symptoms and signs such as erythema nodosum, shortness of breath, malaise, poly arthritis, hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, enlargement of the liver and spleen ( hepatosplenomegaly) and fever.
Sarcoidosis may affect organs such as eyes, skin, lymph nodes, spleen, lung, liver, salivary gland and bone marrow.
Sarcoidosis is common in African american women and west european women age 20 - 40 years old. Laboratory investigations may reveal increase in ACE level, ESR and decreased in the total lung capacity, reduced sensitivity to antigens skin test and hypergammaglobulinemia. Chest x ray may reveal infiltration of the interstitium and bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy.
Sarcoidosis may present with non caseating granuloma. There is a fibrotic center with Langhan giant cells and epithelioid cells. Schaumann bodies and asteroid bodies may also present.
The treatment of sarcoidosis may include corticosteroids.
