|
|
Pathology definition - Polycystic Kidney Disease
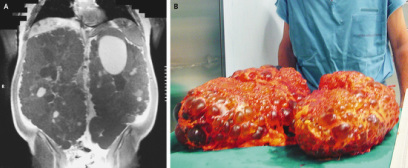
Polycystic Kidney disease
Polycystic kidney disease consists of adult polycystic kidney disease and infantile polycystic kidney disease.
Adult polycystic kidney disease may present with palpable renal mass, hematuria and hypertension. Adult polycystic kidney disease may occur with replacement of the bilateral renal parenchyma with multiple large cyst which is detected with CT scan. The treatment may include symptomatic /supportive therapy with the aim to slow the progression into end stage renal failure. This therapy include controlling blood pressure and low protein diet. Adult polycystic kidney disease is an autosomal dominant disorder which is due to mutation on chromosome no 16 that coded for APKD 1gene. Adult polycystic kidney disease may be associated with berry aneurysm, polycystic liver disease, polycythemia and mitral valve prolapse.
Infantile polycystic kidney disease may present as small homogenous cysts which are separated from the collecting system. Infantile polycystic kidney disease is an autosomal recessive disorder. CT scan may reveal the present of cysts at birth.
References
1.Watson, Michael L., Anne M. Macnicol, and Alan F. Wright. "Adult polycystic kidney disease." BMJ: British Medical Journal 300.6717 (1990): 62.
2.Zerres, Klaus, et al. "Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease." Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 11.supp6 (1996): 29-33.
Polycystic kidney disease consists of adult polycystic kidney disease and infantile polycystic kidney disease.
Adult polycystic kidney disease may present with palpable renal mass, hematuria and hypertension. Adult polycystic kidney disease may occur with replacement of the bilateral renal parenchyma with multiple large cyst which is detected with CT scan. The treatment may include symptomatic /supportive therapy with the aim to slow the progression into end stage renal failure. This therapy include controlling blood pressure and low protein diet. Adult polycystic kidney disease is an autosomal dominant disorder which is due to mutation on chromosome no 16 that coded for APKD 1gene. Adult polycystic kidney disease may be associated with berry aneurysm, polycystic liver disease, polycythemia and mitral valve prolapse.
Infantile polycystic kidney disease may present as small homogenous cysts which are separated from the collecting system. Infantile polycystic kidney disease is an autosomal recessive disorder. CT scan may reveal the present of cysts at birth.
References
1.Watson, Michael L., Anne M. Macnicol, and Alan F. Wright. "Adult polycystic kidney disease." BMJ: British Medical Journal 300.6717 (1990): 62.
2.Zerres, Klaus, et al. "Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease." Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 11.supp6 (1996): 29-33.
