Pathology definition - Common Variable Immunodeficiency
Common variable immunodeficiency
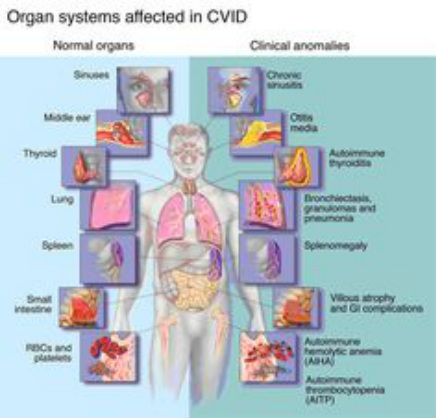
Common variable immunodeficiency may affect adolescence mostly. Patient may present with recurrent episodes of pyogenic infection. There is also a possibilities of developing neoplastic condition or present with gastrointestinal syndrome. In this case patient is treated with intravenous antibodies and gamma globulin therapy.
Patient with common variable immunodeficiency may present with defect in the intrinsic pathway of the B cell which stop the terminal maturation into antibody - secreting plasma cell. There will be deficiency of the synthesis of the antibody. Investigation may reveal decreased in the level of IgG initially. At the end all classes of antibody will be affected.
There will be non caseating granuloma present in the liver, lung, spleen and skin. The common complication of common variable immunodeficiency are carcinoma of stomach/gastric carcinoma, B cell neoplasm and skin cancer.
Common variable immunodeficiency may affect adolescence mostly. Patient may present with recurrent episodes of pyogenic infection. There is also a possibilities of developing neoplastic condition or present with gastrointestinal syndrome. In this case patient is treated with intravenous antibodies and gamma globulin therapy.
Patient with common variable immunodeficiency may present with defect in the intrinsic pathway of the B cell which stop the terminal maturation into antibody - secreting plasma cell. There will be deficiency of the synthesis of the antibody. Investigation may reveal decreased in the level of IgG initially. At the end all classes of antibody will be affected.
There will be non caseating granuloma present in the liver, lung, spleen and skin. The common complication of common variable immunodeficiency are carcinoma of stomach/gastric carcinoma, B cell neoplasm and skin cancer.
