Pathology definition - Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax
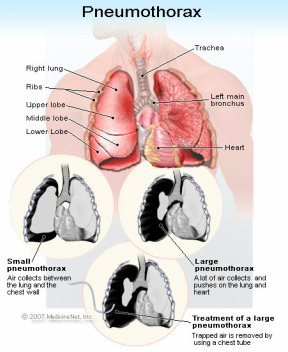
Pneumothorax is the present of the air in the pleural space. There are two forms of pneumothorax. Primary pneumothorax, secondary pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax. Commonly pneumothorax may in patient who is thin and tall. ( Marfan syndrome association).
Primary pneumothorax may occur due to penetrating trauma, blunt trauma or rupture of the subpleural bleb. Secondary pneumothorax may occur due to complication of other lung disorder such as cystic fibrosis, tuberculosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Tension pneumothorax may occur due to positive pressure mechanical ventilation.
Patient with pneumothorax may present with symptoms and signs such as shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, hyperresonance to lung percussion, decreased breath sound and decreased in tactile fremitus. The tracheal may also be deviated away from the sides of pneumothorax.
The air that present in the pleural space may lead to collapse and compression of the lung. The treatment may include surgical resection of any blebs that may present and drainage of the air with chest tube. Chest x ray may reveal an abnormally radiolucent costophrenic sulcus ( deep sulcus) and the present of visceral pleural line.
Pneumothorax is the present of the air in the pleural space. There are two forms of pneumothorax. Primary pneumothorax, secondary pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax. Commonly pneumothorax may in patient who is thin and tall. ( Marfan syndrome association).
Primary pneumothorax may occur due to penetrating trauma, blunt trauma or rupture of the subpleural bleb. Secondary pneumothorax may occur due to complication of other lung disorder such as cystic fibrosis, tuberculosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Tension pneumothorax may occur due to positive pressure mechanical ventilation.
Patient with pneumothorax may present with symptoms and signs such as shortness of breath, pleuritic chest pain, hyperresonance to lung percussion, decreased breath sound and decreased in tactile fremitus. The tracheal may also be deviated away from the sides of pneumothorax.
The air that present in the pleural space may lead to collapse and compression of the lung. The treatment may include surgical resection of any blebs that may present and drainage of the air with chest tube. Chest x ray may reveal an abnormally radiolucent costophrenic sulcus ( deep sulcus) and the present of visceral pleural line.
