|
|
Pathology definition - Viral meningitis
Viral meningitis
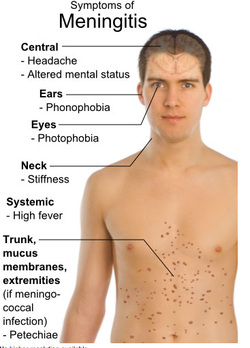
Viral meningitis is another form of meningitis besides bacterial/pyogenic meningitis. Viral meningitis is presented with symptoms and signs such as neck stiffness, photophobia, headache and fever. The common causes of viral meningitis are due to mumps virus, Coxsackie virus and echovirus.
Viral meningitis may present with mild edema and mild lymphocytic infiltration to the subarachnoid space. Lumbar puncture is performed and the analysis reveal the present of normal level of glucose, slight elevation of the level of the protein and also lymphocytosis. No specific treatment is required in treating viral meningitis. Viral meningitis is self limiting illness. The treatment is supportive therapy and treating the precipitating factors.
References
1.Rotbart, Harley A. “Viral Meningitis.” Seminars in Neurology Volume 20, no. Number 03 (2000): 277–292. doi:10.1055/s-2000-9427.
Ratzan, K R. “Viral Meningitis.” The Medical Clinics of North America 69, no. 2 (March 1985): 399–413.
Viral meningitis is another form of meningitis besides bacterial/pyogenic meningitis. Viral meningitis is presented with symptoms and signs such as neck stiffness, photophobia, headache and fever. The common causes of viral meningitis are due to mumps virus, Coxsackie virus and echovirus.
Viral meningitis may present with mild edema and mild lymphocytic infiltration to the subarachnoid space. Lumbar puncture is performed and the analysis reveal the present of normal level of glucose, slight elevation of the level of the protein and also lymphocytosis. No specific treatment is required in treating viral meningitis. Viral meningitis is self limiting illness. The treatment is supportive therapy and treating the precipitating factors.
References
1.Rotbart, Harley A. “Viral Meningitis.” Seminars in Neurology Volume 20, no. Number 03 (2000): 277–292. doi:10.1055/s-2000-9427.
Ratzan, K R. “Viral Meningitis.” The Medical Clinics of North America 69, no. 2 (March 1985): 399–413.
