Symptom finder - The causes of pruritus
Symptom finder - The causes of pruritus
Pruritus is itchiness of the skin. There are 2 causes of pruritus. Dermatological causes of pruritus and generalized causes of pruritus. Dermatological causes of pruritus are visible on inspection.
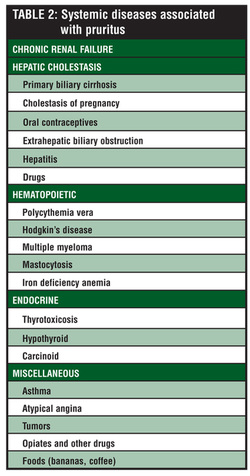
Generalized causes of pruritus are diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism ( endocrine disorder), Hodgkin lymphoma and bronchogenic carcinoma ( malignancy), withdrawal of alcohol or drug withdrawal, opiates due to the release of histamine and cholestasis due to oral contraceptive pills ( drug causes) and polycythemia or iron deficiency anemia ( hematological causes) and general causes such as chronic renal failure and obstructive jaundice.
Initially, history should focus on the site and nature of the pruritus. Ask the patient regarding any drug intake which initiate the development of pruritus ( rule out medication induced pruritus). Explore the patient alcohol status. Any withdrawal of alcohol or certain drugs. Evaluate the patient thoroughly especially if he develop symptoms of blood loss as iron deficiency anemia due to blood loss may cause pruritus. Pruritus that develop after hot bath is an indication of polycythemia.
Underlying features of bronchogenic carcinoma such as smoker who develop chronic cough, hemoptysis and loss of weight should be recorded. Hodgkin’s lymphoma is more prominent with weight loss, night sweat, fever and localized lymphadenopathy. Accumulation of bile salt in obstructive jaundice may also cause pruritus. Besides yellow discoloration due to jaundice patient may present with dark urine and pale stool.
Chronic renal failure may present with multi systemic features such as pain in the bone, edema, skin fragility, hematuria, polyuria, oliguria, nocturia, anorexia, lethargy and frothy urine from proteinuria. Thyroid disease may also cause pruritus. Clinical features of hypothyroidism may include menorrhagia, constipation, weight gain, mental slowing and cold intolerance. Clinical features of hypothyroidism may include diarrhea, anxiety, increase appetite, loss of weight, palpitation, tremor and heat intolerance.
On inspection, the patient’ eye will show changes that include wide starring and lid lag. This is a characteristic of thyrotoxicosis besides tremor . Facial plethora and insufflation of conjunctiva are the characteristic of polycythemia. Severe cases of anemia may present with conjunctival pallor. The present of jaundice is obvious by observing the color of the sclera. Uremic frost, easy bruising and sallow skin are the characteristic of chronic renal failure. Bronchial carcinoma may present with clubbing. Angular cheilitis and spoon shaped nail are due to iron deficiency anemia.
Abdominal and lymphatic examination are useful for cases of lymphoma or malignancy that present with pruritus. Hodgkin’s lymphoma is prominent with localized lymphadenopathy which is non tender and asymmetrical with the absent of infection. Any nodularity , enlargement of thyroid gland or asymmetrical thyroid gland should be reported. Splenomegaly or enlargement of the spleen will occur due to polycythemia rubra vera or Hodgkin’s lymphoma disease. Apical lung tumor may present with Horner’s syndrome, pleural effusion and lobar collapse of the lung. Partial obstruction of the endoluminal bronchus is presented with monophonic inspiratory wheeze. Mostly in bronchial carcinoma.
Pruritus is itchiness of the skin. There are 2 causes of pruritus. Dermatological causes of pruritus and generalized causes of pruritus. Dermatological causes of pruritus are visible on inspection.
Generalized causes of pruritus are diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism ( endocrine disorder), Hodgkin lymphoma and bronchogenic carcinoma ( malignancy), withdrawal of alcohol or drug withdrawal, opiates due to the release of histamine and cholestasis due to oral contraceptive pills ( drug causes) and polycythemia or iron deficiency anemia ( hematological causes) and general causes such as chronic renal failure and obstructive jaundice.
Initially, history should focus on the site and nature of the pruritus. Ask the patient regarding any drug intake which initiate the development of pruritus ( rule out medication induced pruritus). Explore the patient alcohol status. Any withdrawal of alcohol or certain drugs. Evaluate the patient thoroughly especially if he develop symptoms of blood loss as iron deficiency anemia due to blood loss may cause pruritus. Pruritus that develop after hot bath is an indication of polycythemia.
Underlying features of bronchogenic carcinoma such as smoker who develop chronic cough, hemoptysis and loss of weight should be recorded. Hodgkin’s lymphoma is more prominent with weight loss, night sweat, fever and localized lymphadenopathy. Accumulation of bile salt in obstructive jaundice may also cause pruritus. Besides yellow discoloration due to jaundice patient may present with dark urine and pale stool.
Chronic renal failure may present with multi systemic features such as pain in the bone, edema, skin fragility, hematuria, polyuria, oliguria, nocturia, anorexia, lethargy and frothy urine from proteinuria. Thyroid disease may also cause pruritus. Clinical features of hypothyroidism may include menorrhagia, constipation, weight gain, mental slowing and cold intolerance. Clinical features of hypothyroidism may include diarrhea, anxiety, increase appetite, loss of weight, palpitation, tremor and heat intolerance.
On inspection, the patient’ eye will show changes that include wide starring and lid lag. This is a characteristic of thyrotoxicosis besides tremor . Facial plethora and insufflation of conjunctiva are the characteristic of polycythemia. Severe cases of anemia may present with conjunctival pallor. The present of jaundice is obvious by observing the color of the sclera. Uremic frost, easy bruising and sallow skin are the characteristic of chronic renal failure. Bronchial carcinoma may present with clubbing. Angular cheilitis and spoon shaped nail are due to iron deficiency anemia.
Abdominal and lymphatic examination are useful for cases of lymphoma or malignancy that present with pruritus. Hodgkin’s lymphoma is prominent with localized lymphadenopathy which is non tender and asymmetrical with the absent of infection. Any nodularity , enlargement of thyroid gland or asymmetrical thyroid gland should be reported. Splenomegaly or enlargement of the spleen will occur due to polycythemia rubra vera or Hodgkin’s lymphoma disease. Apical lung tumor may present with Horner’s syndrome, pleural effusion and lobar collapse of the lung. Partial obstruction of the endoluminal bronchus is presented with monophonic inspiratory wheeze. Mostly in bronchial carcinoma.
The investigations may include full blood count, blood film, urea and electrolytes, urine dipstick, chest X ray, thyroid function test, liver function test, glucose, excisional biopsy of lymph nodes, CT chest and abdomen, serum iron, serum ferritin and protopoprhyrin and ultrasound of the abdomen.
In term of full blood count, raised hemoglobin is associated with polycythemia. Hodgkin’s lymphoma is presented with normochromic normocytic anemia. Microcytic hypochromic anemia is associated with iron deficiency anemia. Urea and electrolytes studies may reveal raised serum creatinine and urea in renal failure.
The present of blood and protein in the urine are associated with renal disease. This can be detected by using urine dipstick. Chest x ray may detect the present of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, hilar lymphadenopathy and bronchial carcinoma. Thyrotoxicosis is presented with raised T4 and reduction in TSH ( thyroid stimulating hormone). Hypothyroidism is presented with low T4 and raised TSH level.These values are found while performing the thyroid function test. In obstructive jaundice. liver function test may reveal raised alkaline phosphatase and raised bilirubin. Glucose level is raised in case of diabetes mellitus.
Excisional biopsy of lymph node may reveal the present of Reed- Sternberg cells which are associated with Hodgkin’s lymphoma . CT scan of the abdomen and chest may reveal lesions in the chest due to bronchial carcinoma and hilar lymphadenopathy in lymphoma. Iron deficiency anemia is presented with low serum ferritin, low serum iron and increase in free erythrocytes protoporphyrin. Ultrasound scan of the abdomen may reveal sizes of the kidney which decrease in chronic renal disease, dilated bile ducts due to obstructive jaundice ( sizes and sites of obstruction are visualized) . In polycystic kidney disease , multiple cysts are visible.
In term of full blood count, raised hemoglobin is associated with polycythemia. Hodgkin’s lymphoma is presented with normochromic normocytic anemia. Microcytic hypochromic anemia is associated with iron deficiency anemia. Urea and electrolytes studies may reveal raised serum creatinine and urea in renal failure.
The present of blood and protein in the urine are associated with renal disease. This can be detected by using urine dipstick. Chest x ray may detect the present of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, hilar lymphadenopathy and bronchial carcinoma. Thyrotoxicosis is presented with raised T4 and reduction in TSH ( thyroid stimulating hormone). Hypothyroidism is presented with low T4 and raised TSH level.These values are found while performing the thyroid function test. In obstructive jaundice. liver function test may reveal raised alkaline phosphatase and raised bilirubin. Glucose level is raised in case of diabetes mellitus.
Excisional biopsy of lymph node may reveal the present of Reed- Sternberg cells which are associated with Hodgkin’s lymphoma . CT scan of the abdomen and chest may reveal lesions in the chest due to bronchial carcinoma and hilar lymphadenopathy in lymphoma. Iron deficiency anemia is presented with low serum ferritin, low serum iron and increase in free erythrocytes protoporphyrin. Ultrasound scan of the abdomen may reveal sizes of the kidney which decrease in chronic renal disease, dilated bile ducts due to obstructive jaundice ( sizes and sites of obstruction are visualized) . In polycystic kidney disease , multiple cysts are visible.
