|
|
Pathology definition - Hodgkin Lymphoma
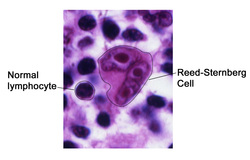
Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma can be divided into different variants based on the histological finding. The first variant is known as lymphocytes predominance which consists of few Reed - Sternberg cells ( Reed Sternberg cell is a multinucleated giant cell that composes of eosinophilic nucleoli which look like owl’s eye. Reed Sternberg cell is originated from B cell) but a lot of lymphocytes. The next variant is known as nodular sclerosis which consists of different variants of Reed - Sternberg cells /lacunar cells as well as fibrous bands. The next variant consists of mixed cellularity that include Reed Sternberg cells, plasma cell,s eosinophils, fibrosis. The last variant is lymphocyte depletion which includes cellular necrosis, a lot of Reed Sternberg cells and few lymphocytes. Hodgkin lymphoma may spread through contiguous lymph nodes.
Hodgkin lymphoma has a bimodal age distribution. Hodgkin lymphoma is common in patient between the age 20 - 30 and 50 years of age,
The prognosis of Hodgkin lymphoma is good with high percentage of cure rate if there is absence of fever, night sweat, loss of weight and no disseminated disease as well as histological variants consists of nodular sclerosis and lymphocytes depletion.
Epstein Barr virus is known as one of the common caused of Hodgkin lymphoma. The common presentation signs and symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma are B symptoms ( loss weight, night sweats and fever ), pruritus, painless lymphadenopathy in the neck and splenomegaly. The treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma is through radiation as well as chemotherapy.
References
1.Weiss, Lawrence M., Lucile A. Movahed, Roger A. Warnke, and Jeffrey Sklar. “Detection of Epstein–Barr Viral Genomes in Reed–Sternberg Cells of Hodgkin’s Disease.” New England Journal of Medicine 320, no. 8 (1989): 502–506. doi:10.1056/NEJM198902233200806.
2.Haluska, F. G., A. M. Brufsky, and G. P. Canellos. “The Cellular Biology of the Reed-Sternberg Cell [see Comments].” Blood 84, no. 4 (August 15, 1994): 1005–1019.
Hodgkin lymphoma can be divided into different variants based on the histological finding. The first variant is known as lymphocytes predominance which consists of few Reed - Sternberg cells ( Reed Sternberg cell is a multinucleated giant cell that composes of eosinophilic nucleoli which look like owl’s eye. Reed Sternberg cell is originated from B cell) but a lot of lymphocytes. The next variant is known as nodular sclerosis which consists of different variants of Reed - Sternberg cells /lacunar cells as well as fibrous bands. The next variant consists of mixed cellularity that include Reed Sternberg cells, plasma cell,s eosinophils, fibrosis. The last variant is lymphocyte depletion which includes cellular necrosis, a lot of Reed Sternberg cells and few lymphocytes. Hodgkin lymphoma may spread through contiguous lymph nodes.
Hodgkin lymphoma has a bimodal age distribution. Hodgkin lymphoma is common in patient between the age 20 - 30 and 50 years of age,
The prognosis of Hodgkin lymphoma is good with high percentage of cure rate if there is absence of fever, night sweat, loss of weight and no disseminated disease as well as histological variants consists of nodular sclerosis and lymphocytes depletion.
Epstein Barr virus is known as one of the common caused of Hodgkin lymphoma. The common presentation signs and symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma are B symptoms ( loss weight, night sweats and fever ), pruritus, painless lymphadenopathy in the neck and splenomegaly. The treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma is through radiation as well as chemotherapy.
References
1.Weiss, Lawrence M., Lucile A. Movahed, Roger A. Warnke, and Jeffrey Sklar. “Detection of Epstein–Barr Viral Genomes in Reed–Sternberg Cells of Hodgkin’s Disease.” New England Journal of Medicine 320, no. 8 (1989): 502–506. doi:10.1056/NEJM198902233200806.
2.Haluska, F. G., A. M. Brufsky, and G. P. Canellos. “The Cellular Biology of the Reed-Sternberg Cell [see Comments].” Blood 84, no. 4 (August 15, 1994): 1005–1019.
