Symptom finder - The causes of respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
taken from studyblue.com
Symptom finder - The causes of respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
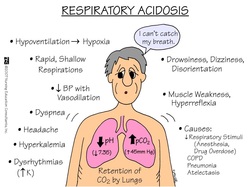
Respiratory acidosis is a condition when there is an accumulation of carbon dioxide as a result of inadequate pulmonary ventilation. In respiratory acidosis, there will be reduction in the pH and elevation of partial pressure of carbon dioxide ( pCO2 ). Respiratory acidosis is followed with compensatory mechanism which include reduction in H+ ( hydrogen ion) by the kidneys and elevated bicarbonate by the bicarbonate buffer system.
Patient with respiratory acidosis may present with symptoms and signs of underlying disorders. Other symptoms include somnolence, lethargy, anxiety, confusion and disorientation. Carbon dioxide retention typically present with bounding pulse and tachycardia. Chest wall deformity or flail chest are also associated with respiratory acidosis. Cyanosis as well as hypotension commonly presented as a severe signs of respiratory acidosis. Papilloedema may also present.
The causes of respiratory acidosis are neuromuscular disorder such as Guillain Barre syndrome , myasthenia gravis, depression of the central nervous system ( due to injury of the head, encephalitis, stroke, coma and drug such as anesthetics or opiates , impaired exchange of the gases such as pulmonary contusions from thoracic injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonia, alveolar disorder or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, skeletal disorder such as flail chest, ankylosing spondylitis and kyphoscoliosis. Unmonitored and uncontrolled artificial ventilation may also cause respiratory acidosis. All causes of hypoventilation may predispose to respiratory acidosis. It is vital to reverse hypoxemia following hypoventilation as it is a life threatening condition. Retention of carbon dioxide may lead to hypercapnia. Rapidly correcting hypercapnia may lead to seizures from alkalinization of the CSF.
The investigation require are arterial blood gases which may reveal increase in bicarbonates ion, pH < 7.35 and pCO2 > 5.8kPa , CT scan or MRI scan of the head ( to locate any lesion on the brainstem), chest x ray ( to identify any pulmonary disorder), nerve conduction test and EMG ( Guillain Barre syndrome and myasthenia gravis) and pulmonary function test ( skeletal disease present as restrictive defect while COPD may present as obstructive defect).
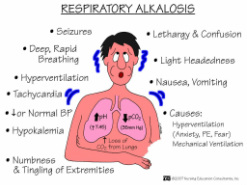
Respiratory alkalosis commonly affecting critically ill patient. Respiratory alkalosis is associated with loss of carbon dioxide through pulmonary ventilation ( increase in pH and decrease in partial pressure of carbon dioxide) excessive in nature. Respiratory alkalosis is associated with compensatory mechanism such as an increase in hydrogen ion by kidney ( several days require. It is a time consuming process) and decrease in bicarbonate ion by bicarbonate buffer system.
Respiratory alkalosis is presented with numbness of the hand and feet, dizziness, circumoral paraesthesia and light headedness. Acutely low carbon dioxide is associated with fits, confusion as well as syncope as a result of cerebral vasoconstriction. Respiratory alkalosis is associated with hyperventilation. One of the common causes of respiratory alkalosis is inadequate monitoring of prolonged artificial ventilation.
Other causes of respiratory alkalosis are drugs such as salicylate, physiological causes such as severe anaemia, high altitude and pregnancy, respiratory disorder such as pulmonary embolism , pulmonary edema and pneumonia, central nervous system disorders such as encephalitis, stoke, head injury, hysteria, anxiety, pain and pyrexia and other remaining causes such as sepsis or overcompensation due to metabolic acidosis.
The investigations require are CT scan or MRI scan of the head to detect for any intracranial lesions, arterial blood gases (pH >7.45, reduction in bicarbonate ions, and pCO2 < 4.4 kPa), serum salicylate measurement and serum calcium ( reduction in calcium level due to increase calcium binding to the albumin).
Respiratory acidosis is a condition when there is an accumulation of carbon dioxide as a result of inadequate pulmonary ventilation. In respiratory acidosis, there will be reduction in the pH and elevation of partial pressure of carbon dioxide ( pCO2 ). Respiratory acidosis is followed with compensatory mechanism which include reduction in H+ ( hydrogen ion) by the kidneys and elevated bicarbonate by the bicarbonate buffer system.
Patient with respiratory acidosis may present with symptoms and signs of underlying disorders. Other symptoms include somnolence, lethargy, anxiety, confusion and disorientation. Carbon dioxide retention typically present with bounding pulse and tachycardia. Chest wall deformity or flail chest are also associated with respiratory acidosis. Cyanosis as well as hypotension commonly presented as a severe signs of respiratory acidosis. Papilloedema may also present.
The causes of respiratory acidosis are neuromuscular disorder such as Guillain Barre syndrome , myasthenia gravis, depression of the central nervous system ( due to injury of the head, encephalitis, stroke, coma and drug such as anesthetics or opiates , impaired exchange of the gases such as pulmonary contusions from thoracic injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonia, alveolar disorder or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, skeletal disorder such as flail chest, ankylosing spondylitis and kyphoscoliosis. Unmonitored and uncontrolled artificial ventilation may also cause respiratory acidosis. All causes of hypoventilation may predispose to respiratory acidosis. It is vital to reverse hypoxemia following hypoventilation as it is a life threatening condition. Retention of carbon dioxide may lead to hypercapnia. Rapidly correcting hypercapnia may lead to seizures from alkalinization of the CSF.
The investigation require are arterial blood gases which may reveal increase in bicarbonates ion, pH < 7.35 and pCO2 > 5.8kPa , CT scan or MRI scan of the head ( to locate any lesion on the brainstem), chest x ray ( to identify any pulmonary disorder), nerve conduction test and EMG ( Guillain Barre syndrome and myasthenia gravis) and pulmonary function test ( skeletal disease present as restrictive defect while COPD may present as obstructive defect).
Respiratory alkalosis commonly affecting critically ill patient. Respiratory alkalosis is associated with loss of carbon dioxide through pulmonary ventilation ( increase in pH and decrease in partial pressure of carbon dioxide) excessive in nature. Respiratory alkalosis is associated with compensatory mechanism such as an increase in hydrogen ion by kidney ( several days require. It is a time consuming process) and decrease in bicarbonate ion by bicarbonate buffer system.
Respiratory alkalosis is presented with numbness of the hand and feet, dizziness, circumoral paraesthesia and light headedness. Acutely low carbon dioxide is associated with fits, confusion as well as syncope as a result of cerebral vasoconstriction. Respiratory alkalosis is associated with hyperventilation. One of the common causes of respiratory alkalosis is inadequate monitoring of prolonged artificial ventilation.
Other causes of respiratory alkalosis are drugs such as salicylate, physiological causes such as severe anaemia, high altitude and pregnancy, respiratory disorder such as pulmonary embolism , pulmonary edema and pneumonia, central nervous system disorders such as encephalitis, stoke, head injury, hysteria, anxiety, pain and pyrexia and other remaining causes such as sepsis or overcompensation due to metabolic acidosis.
The investigations require are CT scan or MRI scan of the head to detect for any intracranial lesions, arterial blood gases (pH >7.45, reduction in bicarbonate ions, and pCO2 < 4.4 kPa), serum salicylate measurement and serum calcium ( reduction in calcium level due to increase calcium binding to the albumin).