Pathology definition - Acute Renal Failure
Acute renal failure
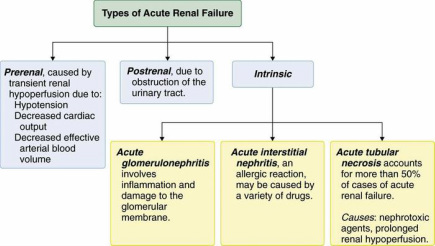
There are three different forms of acute renal failure. Prerenal, intrarenal and postrenal. Prerenal due to hypoperfusion of the renal which leads water and sodium retention due to decreased in glomerular filtration rate. Prerenal renal failure is due to sepsis, congestive heart failure, burns and hypotension. The treatment will focus on electrolytes and fluid management or dialysis.
Intrarenal renal failure may occur due to backflow of fluid across the necrotic tubule and tubule obstruction results from patchy necrosis of the tubules. This will later lead to decrease in glomerular filtration rates.The common causes of intrarenal failure are toxins, acute tubular necrosis and renal ischemia. The treatment will focus on electrolytes and fluid replacement or dialysis.
Postrenal renal failure occur due to neoplasia, kidney stones and benign prostatic hyperplasia which lead to bilateral outflow obstruction. Catheter is used to relive the obstruction.
Generally, patient with acute renal failure may present with anemia, oliguria, hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia.
There are three different forms of acute renal failure. Prerenal, intrarenal and postrenal. Prerenal due to hypoperfusion of the renal which leads water and sodium retention due to decreased in glomerular filtration rate. Prerenal renal failure is due to sepsis, congestive heart failure, burns and hypotension. The treatment will focus on electrolytes and fluid management or dialysis.
Intrarenal renal failure may occur due to backflow of fluid across the necrotic tubule and tubule obstruction results from patchy necrosis of the tubules. This will later lead to decrease in glomerular filtration rates.The common causes of intrarenal failure are toxins, acute tubular necrosis and renal ischemia. The treatment will focus on electrolytes and fluid replacement or dialysis.
Postrenal renal failure occur due to neoplasia, kidney stones and benign prostatic hyperplasia which lead to bilateral outflow obstruction. Catheter is used to relive the obstruction.
Generally, patient with acute renal failure may present with anemia, oliguria, hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia.
