Pathology definition - Breast Carcinoma
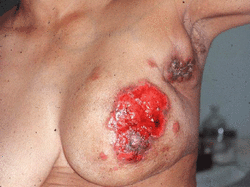
Breast Carcinoma
Patient may present with symptoms and signs such as non tender, fixed painless mass mostly in the upper quadrant of the breast. Patient may also present with palpable lymph nodes. Poor prognosis is associated with high grade ductal carcinoma, overexpression of erb- B2 oncogene and metastasis to the lymph node, liver, lung and bone.
There are few forms of breast carcinoma which may include intraductal comedocarcinoma,
infiltrating ductal carcinoma, infiltrating lobular, mucinous , medullary and Paget disease of the breast.
Paget disease consists of Paget cells which extend from ducts and invade the epidermies of the nipple. Paget disease of the breast may present with painless, itchy, scaly eczematous patches on the nipple.
Medullary breast carcinoma may present with lymphocytic infiltration and solid sheets of cells with large nucleoli. The medullary breast carcinoma is a fleshy soft consistency mass.
Infiltrating lobular breast carcinoma may present with multiple and bilateral mass. Infiltrating lobular breast carcinoma may arise from the lobular carcinoma in situ.There will be Indian file line up of tumor cells which surround the lobule. There will be signet ring cells.
Ductal carcinoma in situ may give rise to infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Infiltrating ductal carcinoma consists of tumor cells embedded in the dense fibrous stroma. The tumor cells are arranged in glands, cords and islands. The mass of the infiltrating ductal carcinoma is fixed and firm.
Mucinous or colloid breast carcinoma may present with collection of the mucin extracellular which surround the cluster of tumor cells.
There is also inflammatory breast carcinoma which may present as orange peel skin appearance with painful red swollen mass.Inflammatory breast carcinoma is associated with lymph nodes involvement.
Intraductal comedocarcinoma present as tumor cells within the duct. There will be inflammation, periductal fibrosis and central necrosis.
Breast carcinoma may present with hypercalcemia due to paraneoplastic syndrome. Paraneoplastic syndrome may associate with breast carcinoma. There will be microcalcification detected on the chest x ray due to paraneoplastic syndrome.
The most common causes of breast carcinoma include positive family history, mutation of the BRCA1 and mutation of the BRCA2, female increase age, early menarche, late menopause, nulliparity and use of estrogen.
The treatment of breast carcinoma may include tamoxifen which acts against the estrogen receptor in the nuclei of the tumor, surgical approach such mastectomy and wide local excision.
Patient may present with symptoms and signs such as non tender, fixed painless mass mostly in the upper quadrant of the breast. Patient may also present with palpable lymph nodes. Poor prognosis is associated with high grade ductal carcinoma, overexpression of erb- B2 oncogene and metastasis to the lymph node, liver, lung and bone.
There are few forms of breast carcinoma which may include intraductal comedocarcinoma,
infiltrating ductal carcinoma, infiltrating lobular, mucinous , medullary and Paget disease of the breast.
Paget disease consists of Paget cells which extend from ducts and invade the epidermies of the nipple. Paget disease of the breast may present with painless, itchy, scaly eczematous patches on the nipple.
Medullary breast carcinoma may present with lymphocytic infiltration and solid sheets of cells with large nucleoli. The medullary breast carcinoma is a fleshy soft consistency mass.
Infiltrating lobular breast carcinoma may present with multiple and bilateral mass. Infiltrating lobular breast carcinoma may arise from the lobular carcinoma in situ.There will be Indian file line up of tumor cells which surround the lobule. There will be signet ring cells.
Ductal carcinoma in situ may give rise to infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Infiltrating ductal carcinoma consists of tumor cells embedded in the dense fibrous stroma. The tumor cells are arranged in glands, cords and islands. The mass of the infiltrating ductal carcinoma is fixed and firm.
Mucinous or colloid breast carcinoma may present with collection of the mucin extracellular which surround the cluster of tumor cells.
There is also inflammatory breast carcinoma which may present as orange peel skin appearance with painful red swollen mass.Inflammatory breast carcinoma is associated with lymph nodes involvement.
Intraductal comedocarcinoma present as tumor cells within the duct. There will be inflammation, periductal fibrosis and central necrosis.
Breast carcinoma may present with hypercalcemia due to paraneoplastic syndrome. Paraneoplastic syndrome may associate with breast carcinoma. There will be microcalcification detected on the chest x ray due to paraneoplastic syndrome.
The most common causes of breast carcinoma include positive family history, mutation of the BRCA1 and mutation of the BRCA2, female increase age, early menarche, late menopause, nulliparity and use of estrogen.
The treatment of breast carcinoma may include tamoxifen which acts against the estrogen receptor in the nuclei of the tumor, surgical approach such mastectomy and wide local excision.
