Pathology definition - Fibrocystic Disease
Fibrocystic Disease
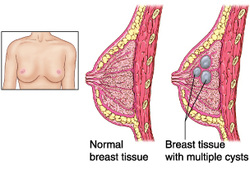
Fibrocystic disease may present with multiple palpable mass mostly bilateral. There will be changes in the sizes of the mass. Patient may complain of mid cycle diffuse pain in the breast.The treatment is mostly symptomatic treatment. Fibrocystic disease of the breast is associated with imbalance of the hormone level . There may be an increase in estrogens and decrease in progesterone.
Fibrocystic disease is the most common form of breast disorder. There are four forms of histological changes which include cystic, epithelial hyperplasia of breast duct, stromal fibrosis and sclerosing adenosis. Cystic may present with blue dome cyst which is lend by polygonal cells. There will be multiple fluid filled cyst with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm. There will be cystic epithelium that appear as papillary projection.There is no risk of developing breast carcinoma/breast cancer.
Breast stroma may undergoes hyperplasia and fibrosis in case of histological pattern of the stromal fibrosis.Stromal fibrosis carries no risk of developing breast carcinoma.
The next histological pattern is the epithelial hyperplasia of the breast duct. This condition may lead to irregular lumen due to increase in the number of epithelial layers in terminal duct lobules. There is a mild risk of developing breast carcinoma.
The final pattern is known as sclerosing adenosis. In this pattern there will be increase in the number of acini. Sclerosing adenosis carries mild risk of developing breast carcinoma/breast cancer.
Fibrocystic disease may present with multiple palpable mass mostly bilateral. There will be changes in the sizes of the mass. Patient may complain of mid cycle diffuse pain in the breast.The treatment is mostly symptomatic treatment. Fibrocystic disease of the breast is associated with imbalance of the hormone level . There may be an increase in estrogens and decrease in progesterone.
Fibrocystic disease is the most common form of breast disorder. There are four forms of histological changes which include cystic, epithelial hyperplasia of breast duct, stromal fibrosis and sclerosing adenosis. Cystic may present with blue dome cyst which is lend by polygonal cells. There will be multiple fluid filled cyst with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm. There will be cystic epithelium that appear as papillary projection.There is no risk of developing breast carcinoma/breast cancer.
Breast stroma may undergoes hyperplasia and fibrosis in case of histological pattern of the stromal fibrosis.Stromal fibrosis carries no risk of developing breast carcinoma.
The next histological pattern is the epithelial hyperplasia of the breast duct. This condition may lead to irregular lumen due to increase in the number of epithelial layers in terminal duct lobules. There is a mild risk of developing breast carcinoma.
The final pattern is known as sclerosing adenosis. In this pattern there will be increase in the number of acini. Sclerosing adenosis carries mild risk of developing breast carcinoma/breast cancer.
