Pathology definition - Thyroid Carcinoma
Thyroid Carcinoma
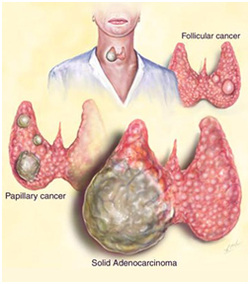
There are four histological forms of carcinoma of the thyroid gland. This includes papillary carcinoma which consists of papillae of the cuboidal cells and the ability to metastases to the lymph nodes. There will also be psammoma bodies and Orphan Annie nuclei.Papillary carcinoma carries the good prognosis.
Other forms include follicular carcinoma which consists of small colloid filled follicle that metastases to the bone and lung via hematogenous spread, anaplastic carcinoma which consists of spindle cells, pleomorphic giant cells that carries the worst/ poor prognosis and anaplastic cells and medullary carcinoma which consists of amyloid deposits and derived from C cells may secrete calcitonin.
The common treatment of carcinoma of the thyroid are radioactive iodine and lobectomy or thyroidectomy. Patient may present with hoarseness of the voice and dsyphagia.
Thyroid carcinoma is associated with genetic predisposition or radiation to the neck and head.
There are four histological forms of carcinoma of the thyroid gland. This includes papillary carcinoma which consists of papillae of the cuboidal cells and the ability to metastases to the lymph nodes. There will also be psammoma bodies and Orphan Annie nuclei.Papillary carcinoma carries the good prognosis.
Other forms include follicular carcinoma which consists of small colloid filled follicle that metastases to the bone and lung via hematogenous spread, anaplastic carcinoma which consists of spindle cells, pleomorphic giant cells that carries the worst/ poor prognosis and anaplastic cells and medullary carcinoma which consists of amyloid deposits and derived from C cells may secrete calcitonin.
The common treatment of carcinoma of the thyroid are radioactive iodine and lobectomy or thyroidectomy. Patient may present with hoarseness of the voice and dsyphagia.
Thyroid carcinoma is associated with genetic predisposition or radiation to the neck and head.
