Pathology definition - Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
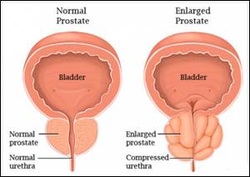
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH may present with nocturia, increase frequency of urination and dysuria as well as hesitancy /difficulty in starting to urinate due to compression of the nodules to the urethra. Benign prostatic hyperplasia occur due to increase in the levels of estradiol mostly in elderly people.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia may present with hyperplasia of the glandular and fibromuscular elements of the stromal. Benign prostatic hyperplasia may present with increase in total PSA. There will be rubbery enlargement of the nodules in the transurethral zone /lateral lobes of the prostate and periurethral zones/ middle lobes of the prostate. There will be increase risk of developing urinary tract infection, bladder hypertrophy and distention, hydronephrosis, hydoureter and urinary obstruction.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia occur due to increase prostatic growth due to expression of receptors for DHT. The treatment will focus more on 5 alpha reductase inhibitor or finasteride and transurethral resection of the prostate.
