Pathology definition - Marfan Syndrome
Marfan Syndrome
Marfan syndrome is a autosomal dominant hereditary disorders. Marfan syndrome may lead to mutation in the chromosome 15 which coded for fibrillin gene. This will led to defect in the extracellular matrix as fibrillin is a glycoprotein which form the microfibrils. As a consequences there will be loss of support from connective tissue or weakening of the vascular wall/ tunica media with risk of tearing of tunica intimal. This will further lead to cystic medial necrosis of aorta.
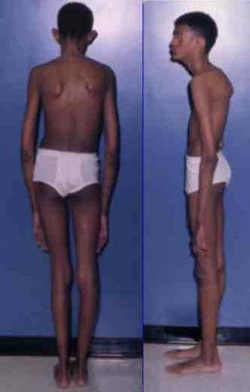
Patient with Marfan syndrome may present with tall stature. They may also present with elongated extremities. Besides that other signs and symptoms may include cystic medial necrosis of the aorta, aortic valve incompetence, aortic aneurysm dissection, prolapse of the mitral valve , dislocation of lenses/ectopia lentis, bilateral subluxation of the lenses, arachnodactyl, hyperextensible joint and kyphosis as well as scoliosis.
The treatment may include cardiology approach ( beta blocker, replacement of the aortic valve, endocarditis prophylaxis) and cardiology surveillance as the common cause of death is related to congestive heart failure or aortic dissection.
Marfan syndrome is a autosomal dominant hereditary disorders. Marfan syndrome may lead to mutation in the chromosome 15 which coded for fibrillin gene. This will led to defect in the extracellular matrix as fibrillin is a glycoprotein which form the microfibrils. As a consequences there will be loss of support from connective tissue or weakening of the vascular wall/ tunica media with risk of tearing of tunica intimal. This will further lead to cystic medial necrosis of aorta.
Patient with Marfan syndrome may present with tall stature. They may also present with elongated extremities. Besides that other signs and symptoms may include cystic medial necrosis of the aorta, aortic valve incompetence, aortic aneurysm dissection, prolapse of the mitral valve , dislocation of lenses/ectopia lentis, bilateral subluxation of the lenses, arachnodactyl, hyperextensible joint and kyphosis as well as scoliosis.
The treatment may include cardiology approach ( beta blocker, replacement of the aortic valve, endocarditis prophylaxis) and cardiology surveillance as the common cause of death is related to congestive heart failure or aortic dissection.
