Pediatric Definition - Acne
Acne
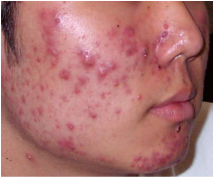
Acne occurs on face, chest and back. Pathologically, acne is associated with increased sebum production, inflammation, proliferation of the bacteria and androgens.
The differential diagnosis of acne may include angiofibromas, rosacea, malaria, molluscum and tuberous sclerosis.
Acne consists of open comedones and closed comedones. Open comedones are blackheads which occur due to oxidization of the melanin within stratum corneum.
Closed comedones are whiteheads due to obstruction of the sebaceous follicle with formation of micromedone later.
The treatment of acne may include general skin care by considering washing with soap twice daily. Antibiotic such as tetracycline, doxycycline or minocycline mostly for pustular cases of acne and topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin for inflammatory lesions. Retinoic acid is considered for comedones. Accutanes for nodulocystics.
Acne occurs on face, chest and back. Pathologically, acne is associated with increased sebum production, inflammation, proliferation of the bacteria and androgens.
The differential diagnosis of acne may include angiofibromas, rosacea, malaria, molluscum and tuberous sclerosis.
Acne consists of open comedones and closed comedones. Open comedones are blackheads which occur due to oxidization of the melanin within stratum corneum.
Closed comedones are whiteheads due to obstruction of the sebaceous follicle with formation of micromedone later.
The treatment of acne may include general skin care by considering washing with soap twice daily. Antibiotic such as tetracycline, doxycycline or minocycline mostly for pustular cases of acne and topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin for inflammatory lesions. Retinoic acid is considered for comedones. Accutanes for nodulocystics.