|
|
Pathology definition - Erythroblastosis Fetalis
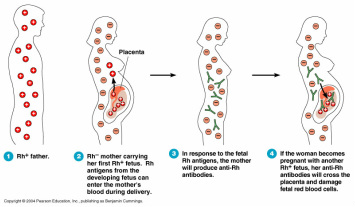
Erythroblastosis fetalis
Peripheral blood smear may reveal reticulocytosis and the present of erythroblast. Erythroblastosis fetalis mostly present due to Rh antigen/ fetal D antigen incompatibility between the mother and the fetus. Erythroblastosis fetalis may also present with ABO incompatibility.
The treatment of the erythroblastosis may include giving anti D IgG to D negative mothers during the delivery period of a child with D positive. Besides that blood transfusion is also given.
Erythroblastosis fetalis may occur due to maternal antibodies reacting against the red blood cell of the fetal. This commonly occur due to maternal alloimmunization to the red blood cell antigen of the fetus which occur due to exposure to the Rh antigens of the fetus during pregnancy.
Patient with erythroblastosis fetalis may present with fetal heart failure, fetal hemolytic anemia, generalized edema, jaundice and kernicterus due to increase in the level of indirect bilirubin and stillbirth.
References
1.Naeye RL. “NEw Observations in Erythroblastosis Fetalis.” JAMA 200, no. 4 (April 24, 1967): 281–286. doi:10.1001/jama.1967.03120170053007.
2.Diamond, Louis K., Victor C. Vaughan, and Fred H. Allen. “ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS III. Prognosis in Relation to Clinical and Serologic Manifestations at Birth.” Pediatrics 6, no. 4 (October 1, 1950): 630–637.
Peripheral blood smear may reveal reticulocytosis and the present of erythroblast. Erythroblastosis fetalis mostly present due to Rh antigen/ fetal D antigen incompatibility between the mother and the fetus. Erythroblastosis fetalis may also present with ABO incompatibility.
The treatment of the erythroblastosis may include giving anti D IgG to D negative mothers during the delivery period of a child with D positive. Besides that blood transfusion is also given.
Erythroblastosis fetalis may occur due to maternal antibodies reacting against the red blood cell of the fetal. This commonly occur due to maternal alloimmunization to the red blood cell antigen of the fetus which occur due to exposure to the Rh antigens of the fetus during pregnancy.
Patient with erythroblastosis fetalis may present with fetal heart failure, fetal hemolytic anemia, generalized edema, jaundice and kernicterus due to increase in the level of indirect bilirubin and stillbirth.
References
1.Naeye RL. “NEw Observations in Erythroblastosis Fetalis.” JAMA 200, no. 4 (April 24, 1967): 281–286. doi:10.1001/jama.1967.03120170053007.
2.Diamond, Louis K., Victor C. Vaughan, and Fred H. Allen. “ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS III. Prognosis in Relation to Clinical and Serologic Manifestations at Birth.” Pediatrics 6, no. 4 (October 1, 1950): 630–637.
