|
|
Pathology definition - Polycythemia vera
Polycythemia vera
Polycythemia vera is part of myeloproliferative disorder besides chronic myeloid leukemia, myelofibrosis and essential thrombocythemia. Polycythemia vera is commonly affecting obese, middle age, hypertensive men. The causes of polycythemia vera is unknown.
Secondary polycythemia occur due to increase erythropoietin activity mostly due to Cushing syndrome, pheochromocytoma, renal failure and chronic hypoxia.
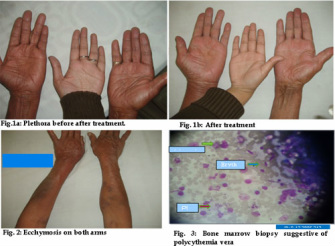
Polycythemia vera is commonly present with signs and symptoms such as thrombosis , pruritus, blurry vision, headache and bleeding problem. Pathologically there will be increase in the myelocytes and megakaryocytes and hypercellular of the bone marrow with increased in the erythroid precursor cells.
The laboratory investigation will reveal an increase in the serum vitamin B12, increase in red blood cell mass, increased in the white blood cell, decreased in the erythropoietin level, increased in the platelet and hyperuricemia. Patient may also present with increased hematocrit and increased in the Hgb. Phlebotomy is the treatment option in case of polycythemia vera.
References
1.Berlin, Nathanial I. “Polycythemia Vera.” Hematology/oncology Clinics of North America 17, no. 5. Accessed December 19, 2013.
2.Ellis, J T, and P Peterson. “The Bone Marrow in Polycythemia Vera.” Pathology Annual 14 Pt 1 (1979): 383–403.
Polycythemia vera is part of myeloproliferative disorder besides chronic myeloid leukemia, myelofibrosis and essential thrombocythemia. Polycythemia vera is commonly affecting obese, middle age, hypertensive men. The causes of polycythemia vera is unknown.
Secondary polycythemia occur due to increase erythropoietin activity mostly due to Cushing syndrome, pheochromocytoma, renal failure and chronic hypoxia.
Polycythemia vera is commonly present with signs and symptoms such as thrombosis , pruritus, blurry vision, headache and bleeding problem. Pathologically there will be increase in the myelocytes and megakaryocytes and hypercellular of the bone marrow with increased in the erythroid precursor cells.
The laboratory investigation will reveal an increase in the serum vitamin B12, increase in red blood cell mass, increased in the white blood cell, decreased in the erythropoietin level, increased in the platelet and hyperuricemia. Patient may also present with increased hematocrit and increased in the Hgb. Phlebotomy is the treatment option in case of polycythemia vera.
References
1.Berlin, Nathanial I. “Polycythemia Vera.” Hematology/oncology Clinics of North America 17, no. 5. Accessed December 19, 2013.
2.Ellis, J T, and P Peterson. “The Bone Marrow in Polycythemia Vera.” Pathology Annual 14 Pt 1 (1979): 383–403.
