|
|
Pathology definition - Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
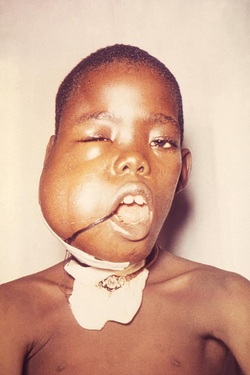
Non Hodgkin lymphoma
Non Hodgkin lymphoma can be divided into a few variants which include follicular B cell, Burkitt B cell, small lymphocytic B cell, mantle cell, diffuse large B cell, marginal cell and MALT lymphoma.
Follicular B cell is caused by proliferation of the cleaved cell in a nodular pattern. Follicular B cell is the commonest variant of the non Hodgkin lymphoma. Burkitt B cell is a non cleaved cells with a starry sky appearance. Small lymphocytes B cell is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia which is consist of small mature lymphocytes that disrupt the architecture of the lymph nodes. There will be a positive mark for CD5 marker. Non Hodgkin lymphoma is not spreading contiguously.
Non Hodgkin lymphoma need to be treated with radiation, chemotherapy and transplant of the bone marrow. The etiology of non Hodgkin lymphoma may include viral infection such as Epstein Barr virus ( commonly leads to development of the Burkitt lymphoma of the jaw). Other cause may include chromosomal translocation such as t ( 8:14) for Burkitt lymphoma which lead to overexpression of the c- myc and t( 14,18) in follicular lymphoma which lead to activation of the bcl-2. Non hodgkin lymphoma carries a poor prognosis especially in the elderly and people with disseminated disease. Laboratory ivestigations may reveal a raise in the lactate dehydrogenase.
Patient may complain of fever, night sweat, weight loss ( B symptoms), lymphadenopathy painless in nature and liver enlargement ( hepatosplenomegaly).
References
1.Melbye, M., K. E. Smedby, and D. Trichopoulos. “Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.” no. Ed.2 (2008): 669–693.
2.Evans, L, and B Hancock. “Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.” The Lancet 362, no. 9378 (July 12, 2003): 139–146. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13868-8.
Non Hodgkin lymphoma can be divided into a few variants which include follicular B cell, Burkitt B cell, small lymphocytic B cell, mantle cell, diffuse large B cell, marginal cell and MALT lymphoma.
Follicular B cell is caused by proliferation of the cleaved cell in a nodular pattern. Follicular B cell is the commonest variant of the non Hodgkin lymphoma. Burkitt B cell is a non cleaved cells with a starry sky appearance. Small lymphocytes B cell is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia which is consist of small mature lymphocytes that disrupt the architecture of the lymph nodes. There will be a positive mark for CD5 marker. Non Hodgkin lymphoma is not spreading contiguously.
Non Hodgkin lymphoma need to be treated with radiation, chemotherapy and transplant of the bone marrow. The etiology of non Hodgkin lymphoma may include viral infection such as Epstein Barr virus ( commonly leads to development of the Burkitt lymphoma of the jaw). Other cause may include chromosomal translocation such as t ( 8:14) for Burkitt lymphoma which lead to overexpression of the c- myc and t( 14,18) in follicular lymphoma which lead to activation of the bcl-2. Non hodgkin lymphoma carries a poor prognosis especially in the elderly and people with disseminated disease. Laboratory ivestigations may reveal a raise in the lactate dehydrogenase.
Patient may complain of fever, night sweat, weight loss ( B symptoms), lymphadenopathy painless in nature and liver enlargement ( hepatosplenomegaly).
References
1.Melbye, M., K. E. Smedby, and D. Trichopoulos. “Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.” no. Ed.2 (2008): 669–693.
2.Evans, L, and B Hancock. “Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.” The Lancet 362, no. 9378 (July 12, 2003): 139–146. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13868-8.
