|
|
Pathology definition - Hydrocephalus
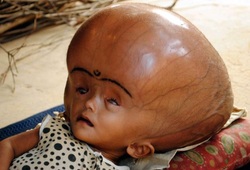
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus may present with signs and symptoms such as large skull in adult, disturbance of the vision, nausea, vomiting, headache, raised intracranial pressure and seizures.
Hydrocephalus occur due increase in volume of the cerebrospinal fluid in the cranium. The accumulation of the cerebrospinal fluid may occur due to mass such as tumor which obstruct the flow of the cerebrospinal fluid or the present of choroid plexus tumor which lead to the overproduction of the cerebrospinal fluid.
There are four categories of hydrocephalus that includes internal hydrocephalus which is due to the excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system. The second variants is the external hydrocephalus which due to accumulation of the excessive cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space. The third variant is communicating hydrocephalus which is caused by the flows of cerebrospinal fluid between subarachnoid spaces and ventricles. Non communicating hydrocephalus is due to obstruction of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid Hydrocephalus ex vacuo is a form of hydrocephalus due to dilation of the ventricles which is most commonly associated with Alzheimer disease and cerebral infarction. There will also be a loss of the brain tissue in this case.
The treatment of hydrocephalus may include removal of the mass which lead to obstruction ( tumor of the choroid plexus) and the insertion of the ventriculoperitoneal shunt.
References
1.Matsumoto, Satoshi. Hydrocephalus: Pathogenesis and Treatment. Springer Verlag, 1991.
2.Richard H. Ames. “Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunts in the Management of Hydrocephalus*.” Research-article.
Hydrocephalus may present with signs and symptoms such as large skull in adult, disturbance of the vision, nausea, vomiting, headache, raised intracranial pressure and seizures.
Hydrocephalus occur due increase in volume of the cerebrospinal fluid in the cranium. The accumulation of the cerebrospinal fluid may occur due to mass such as tumor which obstruct the flow of the cerebrospinal fluid or the present of choroid plexus tumor which lead to the overproduction of the cerebrospinal fluid.
There are four categories of hydrocephalus that includes internal hydrocephalus which is due to the excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system. The second variants is the external hydrocephalus which due to accumulation of the excessive cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space. The third variant is communicating hydrocephalus which is caused by the flows of cerebrospinal fluid between subarachnoid spaces and ventricles. Non communicating hydrocephalus is due to obstruction of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid Hydrocephalus ex vacuo is a form of hydrocephalus due to dilation of the ventricles which is most commonly associated with Alzheimer disease and cerebral infarction. There will also be a loss of the brain tissue in this case.
The treatment of hydrocephalus may include removal of the mass which lead to obstruction ( tumor of the choroid plexus) and the insertion of the ventriculoperitoneal shunt.
References
1.Matsumoto, Satoshi. Hydrocephalus: Pathogenesis and Treatment. Springer Verlag, 1991.
2.Richard H. Ames. “Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunts in the Management of Hydrocephalus*.” Research-article.
