Pathology definition - Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Respiratory distress syndrome
There are two form of respiratory distress syndrome adult respiratory distress syndrome and neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
Adult respiratory distress syndrome may present with cyanosis, pulmonary crackles, shortness of breath and increase in respiratory rates. Adult respiratory distress syndrome may occur due to pancreatitis, overdose of drug, trauma, sepsis and lung infection. The lung will appear red and heavy.
Adult respiratory distress syndrome may present with mismatch ventilation perfusion scan and chest x ray may reveal diffuse bilateral lung infiltration. Adult respiratory distress syndrome occurs due to the damage of the alveolar walls and alveolar capillary walls . This occur due to the action of the endotoxins and cytokines which increase the vascular permeability. There will also be decreased in surfactant that leads to collapse of the alveolar and pulmonary edema as well as inflammation of the hyaline membrane.
Positive pressure mechanical ventilation is considered as the treatment of adult respiratory distress syndrome.
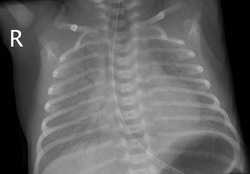
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may present with purple, heavy lung.Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may present with cyanosis, shortness of breath and increase in respiratory rates after birth. Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may occur due to deficiency of the pulmonary surfactant, C- section birth, prematurity and diabetic mother.
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may present with increased in surface tension in the lung due to deficiency of the surfactant which lead to collapse of the lung. There will be an engorged pulmonary vessels. There will also be eosinophilic hyaline membranes within the alveoli.
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may be treated with corticosteroids given to the mother before birth. Oxygen therapy is given. Besides that , exogenous surfactant may be given at birth to infants under 28 weeks.
The common complication of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may include patent ductus arteriosus, necrotizing enterocolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and intraventricular brain hemorrhage.
There are two form of respiratory distress syndrome adult respiratory distress syndrome and neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
Adult respiratory distress syndrome may present with cyanosis, pulmonary crackles, shortness of breath and increase in respiratory rates. Adult respiratory distress syndrome may occur due to pancreatitis, overdose of drug, trauma, sepsis and lung infection. The lung will appear red and heavy.
Adult respiratory distress syndrome may present with mismatch ventilation perfusion scan and chest x ray may reveal diffuse bilateral lung infiltration. Adult respiratory distress syndrome occurs due to the damage of the alveolar walls and alveolar capillary walls . This occur due to the action of the endotoxins and cytokines which increase the vascular permeability. There will also be decreased in surfactant that leads to collapse of the alveolar and pulmonary edema as well as inflammation of the hyaline membrane.
Positive pressure mechanical ventilation is considered as the treatment of adult respiratory distress syndrome.
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may present with purple, heavy lung.Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may present with cyanosis, shortness of breath and increase in respiratory rates after birth. Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may occur due to deficiency of the pulmonary surfactant, C- section birth, prematurity and diabetic mother.
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may present with increased in surface tension in the lung due to deficiency of the surfactant which lead to collapse of the lung. There will be an engorged pulmonary vessels. There will also be eosinophilic hyaline membranes within the alveoli.
Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may be treated with corticosteroids given to the mother before birth. Oxygen therapy is given. Besides that , exogenous surfactant may be given at birth to infants under 28 weeks.
The common complication of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome may include patent ductus arteriosus, necrotizing enterocolitis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and intraventricular brain hemorrhage.
