Pathology definition - Myotonic Dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy is an autosomal dominant disorder. Myotonic dystrophy is associated with an increase in the CTG repeats due to mutation in the myotonin protein kinase gene on chromosome 19.There is a strong anticipation effect. The number of repeats increase with each successive generation making a more severe and serious manifestation of the disease.
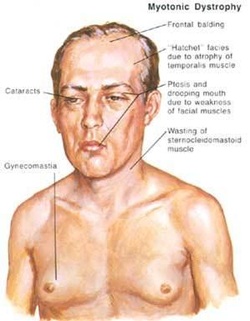
Patient with myotonic dystrophy may present with wasting and weakness of the facial muscle and distal limbs. There will be an increase in muscle stiffness and myotonia is common. Patient is recommended to be treated with phenytoin to relieve the myotonia.
Myotonic dystrophy commonly present with necrosis of the intrafusal fibers of the muscle spindles. There will be splitting of the fiber and the present of cytoplasmic band within the fiber center ( ring fiber) and increase in the number of muscle internal nuclei.
The common complication of myotonic dystrophy are baldness,testicular atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance and cataracts.
Myotonic dystrophy is an autosomal dominant disorder. Myotonic dystrophy is associated with an increase in the CTG repeats due to mutation in the myotonin protein kinase gene on chromosome 19.There is a strong anticipation effect. The number of repeats increase with each successive generation making a more severe and serious manifestation of the disease.
Patient with myotonic dystrophy may present with wasting and weakness of the facial muscle and distal limbs. There will be an increase in muscle stiffness and myotonia is common. Patient is recommended to be treated with phenytoin to relieve the myotonia.
Myotonic dystrophy commonly present with necrosis of the intrafusal fibers of the muscle spindles. There will be splitting of the fiber and the present of cytoplasmic band within the fiber center ( ring fiber) and increase in the number of muscle internal nuclei.
The common complication of myotonic dystrophy are baldness,testicular atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance and cataracts.
