Symptom finder - The causes of sore throat
Symptom finder - The causes of sore throat
The causes of sore throat are inflammatory such as thyroiditis, neurological causes such as glossopharyngeal neuralgia, infection such as quinsy, viral associated pharyngitis or fungal associated pharyngitis, tonsillitis due to glandular fever ( viral tonsillitis) and streptococcus or gonococcus tonsillitis ( bacterial tonsillitis).
Other causes of sore throat are referred pain due to esophageal spasm and angina, neoplasm such as lymphoma, hematological disorder and carcinoma such as laryngeal carcinoma , carcinoma of the posterior third of the tongue and tonsil carcinoma. In an elderly, episodes of prolonged and persistent sore throat are indication of malignancy. AIDS and reflux esophagitis are also associated with sore throat.
Sore throat is a common disorder affecting children and young adults. Prolonged case of sore throat in elderly is associated with malignancy . Besides malignancy, sore throat is also the first presenting symptoms of other disorders such as agranulocytosis and diabetes.
Subacute thyroiditis is a rare condition. Subacute thyroiditis is presented as pain in the neck, malaise, weakness, fever and swelling of the thyroid gland. Patient may also complain of stabbing, sharp pain, at the root of the tongue which radiates to the ear and throat. This condition is known as glossopharyngeal neuralgia and trigger by touching of the pharynx and swallowing.
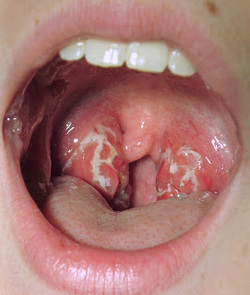
Peritonsillar abscess or quinsy is presented as acute tonsillitis. In this condition, the patient is pyrexial ( high temperature) difficult to swallow ( dysphagia) and referred pain to the ear. Generally infective tonsillitis is presented with malaise , referred pain to the ear, headache, dysphagia and sore throat. Lymphadenopathy, malaise and membranous tonsillitis are common symptoms of glandular fever. Oropharyngeal gonorrhea is associated with oral sex.
AIDS may also cause sore throat due to viral or fungal infections. Sensation of lump in the throat and burning pain are common features of reflux esophagitis. Exercise and pain in the throat are due to angina. Besides that, angina is commonly associated with radiation of pain form the jaw down to the left arm. Besides angina, chest pain that radiates to the jaw or throat is associated with diffuse esophageal spasms.
Lymphoma of the tonsil is commonly present as painless tonsil enlargement. Pain that is referred to the ear, blood spitting, difficulty swallowing and soreness of the tongue are common symptoms of carcinoma of the posterior third of the tongue. Carcinoma of the tonsil is presented as lump in the neck ( occasionally due to metastatic cervical lymphadenopathy) , blood spitting, referred pain to the ear and painful ulcer with induration. Neutropenia may lead to blood dyscrasia. Blood dyscrasia and sore throat occur due to infection as a result of neutropenia.
The causes of sore throat are inflammatory such as thyroiditis, neurological causes such as glossopharyngeal neuralgia, infection such as quinsy, viral associated pharyngitis or fungal associated pharyngitis, tonsillitis due to glandular fever ( viral tonsillitis) and streptococcus or gonococcus tonsillitis ( bacterial tonsillitis).
Other causes of sore throat are referred pain due to esophageal spasm and angina, neoplasm such as lymphoma, hematological disorder and carcinoma such as laryngeal carcinoma , carcinoma of the posterior third of the tongue and tonsil carcinoma. In an elderly, episodes of prolonged and persistent sore throat are indication of malignancy. AIDS and reflux esophagitis are also associated with sore throat.
Sore throat is a common disorder affecting children and young adults. Prolonged case of sore throat in elderly is associated with malignancy . Besides malignancy, sore throat is also the first presenting symptoms of other disorders such as agranulocytosis and diabetes.
Subacute thyroiditis is a rare condition. Subacute thyroiditis is presented as pain in the neck, malaise, weakness, fever and swelling of the thyroid gland. Patient may also complain of stabbing, sharp pain, at the root of the tongue which radiates to the ear and throat. This condition is known as glossopharyngeal neuralgia and trigger by touching of the pharynx and swallowing.
Peritonsillar abscess or quinsy is presented as acute tonsillitis. In this condition, the patient is pyrexial ( high temperature) difficult to swallow ( dysphagia) and referred pain to the ear. Generally infective tonsillitis is presented with malaise , referred pain to the ear, headache, dysphagia and sore throat. Lymphadenopathy, malaise and membranous tonsillitis are common symptoms of glandular fever. Oropharyngeal gonorrhea is associated with oral sex.
AIDS may also cause sore throat due to viral or fungal infections. Sensation of lump in the throat and burning pain are common features of reflux esophagitis. Exercise and pain in the throat are due to angina. Besides that, angina is commonly associated with radiation of pain form the jaw down to the left arm. Besides angina, chest pain that radiates to the jaw or throat is associated with diffuse esophageal spasms.
Lymphoma of the tonsil is commonly present as painless tonsil enlargement. Pain that is referred to the ear, blood spitting, difficulty swallowing and soreness of the tongue are common symptoms of carcinoma of the posterior third of the tongue. Carcinoma of the tonsil is presented as lump in the neck ( occasionally due to metastatic cervical lymphadenopathy) , blood spitting, referred pain to the ear and painful ulcer with induration. Neutropenia may lead to blood dyscrasia. Blood dyscrasia and sore throat occur due to infection as a result of neutropenia.
On examination, diffuse, tender, swelling of the thyroid gland that moves on swallowing is an indication of thyroiditis. Neurological condition such as glossopharyngeal neuralgia is diagnosed based on history and touching of the palate with hope to trigger the symptoms.
History is important in diagnosing reflux esophagitis, esophageal spasm and angina. Other signs of AIDS should be identified such as Kaposi’s sacroma , chest infection, loss of weight, fever and malaise. Viral infection or fungal infection may cause tonsillitis and pharyngitis which is part of the spectrum of AIDS.
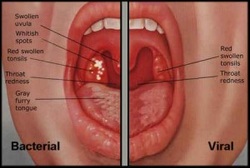
Infective tonsillitis is presented with fetor, pyrexia and pus exuding from tonsillar crypts. Besides that, cervical lymphadenopathy may also present. In glandular fever, splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy may occur elsewhere. Quinsy is characterized by edematous uvula, tonsil which is medially push downwards and trismus.
The investigations require include full blood count , viral antibodies, chest x ray , ECG, ESR, swabs, HIV test, OGD, indirect laryngoscopy, biopsy and CT scan.
Full blood count may reveal low hemoglobin level ( anemia ) as a result of malignancy. Lymphocytosis occur as a result of glandular fever and blood dyscrasia. Glandular fever is also best identified by viral antibodies. Any metastasis of cancer can be detected with chest-x ray. ECG is useful to detect cardiac ischemia. Malignancy, infection and thyroiditis are confirmed with raised ESR. Throat swab ( culture and sensitivity) is only use for persistent and recurrent cases to detect the present of gonococcus and streptococcus .HIV testing is useful for detection of AIDS. Hiatus hernia and esophagitis are visualized with OGD. Indirect laryngoscopy is useful for malignancy and infection. Biopsy is performed to classify any growth as malignant or benign. CT scan is useful to identify the tumor and the spread of the tumor.
History is important in diagnosing reflux esophagitis, esophageal spasm and angina. Other signs of AIDS should be identified such as Kaposi’s sacroma , chest infection, loss of weight, fever and malaise. Viral infection or fungal infection may cause tonsillitis and pharyngitis which is part of the spectrum of AIDS.
Infective tonsillitis is presented with fetor, pyrexia and pus exuding from tonsillar crypts. Besides that, cervical lymphadenopathy may also present. In glandular fever, splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy may occur elsewhere. Quinsy is characterized by edematous uvula, tonsil which is medially push downwards and trismus.
The investigations require include full blood count , viral antibodies, chest x ray , ECG, ESR, swabs, HIV test, OGD, indirect laryngoscopy, biopsy and CT scan.
Full blood count may reveal low hemoglobin level ( anemia ) as a result of malignancy. Lymphocytosis occur as a result of glandular fever and blood dyscrasia. Glandular fever is also best identified by viral antibodies. Any metastasis of cancer can be detected with chest-x ray. ECG is useful to detect cardiac ischemia. Malignancy, infection and thyroiditis are confirmed with raised ESR. Throat swab ( culture and sensitivity) is only use for persistent and recurrent cases to detect the present of gonococcus and streptococcus .HIV testing is useful for detection of AIDS. Hiatus hernia and esophagitis are visualized with OGD. Indirect laryngoscopy is useful for malignancy and infection. Biopsy is performed to classify any growth as malignant or benign. CT scan is useful to identify the tumor and the spread of the tumor.
