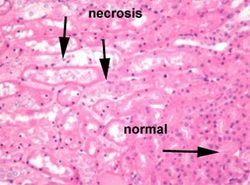
Acute Tubular Necrosis
Acute tubular necrosis may present with oliguria, muddy brown cast in the urine ( tubular epithelial cells), azotemia, hyperkalemia and raised of sodium level in the urine. The common complication of acute tubular necrosis is acute renal failure.
Acute tubular necrosis may present with necrosis of the focal tubular epithelium. There will be rupture of the basement membrane with the present of eosinophilic hyaline casts in the collecting ducts. Besides that, there will be edematous interstitium with flattened epithelium and increase in mitosis ( regeneration of the epithelium).
Acute tubular necrosis may be treated with fluid and electrolytes replacement therapy. Loop diuretics may also considered as well as dialysis.
The common causes of acute tubular necrosis are intense exercise, myoglobinuria ( crush injury), shock, prolonged hypertension, renal ischemia and aminoglycosides which is an nephrotoxic drug. Death may occur following arrhythmias due to hyperkalemia.
Acute tubular necrosis may present with oliguria, muddy brown cast in the urine ( tubular epithelial cells), azotemia, hyperkalemia and raised of sodium level in the urine. The common complication of acute tubular necrosis is acute renal failure.
Acute tubular necrosis may present with necrosis of the focal tubular epithelium. There will be rupture of the basement membrane with the present of eosinophilic hyaline casts in the collecting ducts. Besides that, there will be edematous interstitium with flattened epithelium and increase in mitosis ( regeneration of the epithelium).
Acute tubular necrosis may be treated with fluid and electrolytes replacement therapy. Loop diuretics may also considered as well as dialysis.
The common causes of acute tubular necrosis are intense exercise, myoglobinuria ( crush injury), shock, prolonged hypertension, renal ischemia and aminoglycosides which is an nephrotoxic drug. Death may occur following arrhythmias due to hyperkalemia.
