Pathology definition - Prostate Carcinoma
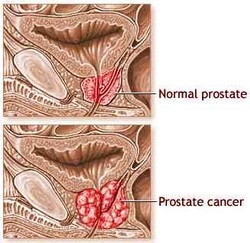
Prostate Carcinoma
Prostate carcinoma may present with symptoms and signs such as dysuria, back pain and increase frequency of urination.
Prostate carcinoma is mostly adenocarcinoma. It is lined by cuboidal cells, large nuclei and nucleoli and consists of well defined gland. Prostate carcinoma may present with invasion of the lymphatic vessel and vascular vessel of prostatic capsule.
Prostate carcinoma may present with raised in prostatic acid phosphatase and raised in serum PSA. There will also be an increase in alkaline phosphatase level in case of bone metastasis.
Prostate carcinoma may spread to the bone via hematogenous spread which later lead to bony osteoblastic metastasis. Prostate carcinoma is graded based on the Gleason system of grading. Prostate carcinoma may occur as irregular, enlarged, firm nodules which is based diagnosed on by performing digital rectal examination and confirm with biopsy of the prostate gland. These nodules may arise from the peripheral zone of the posterior lobe of the prostate glands.
The treatment of prostate carcinoma may include radiotherapy, prostatectomy and anti androgen / flutamide.
Prostate carcinoma may present with symptoms and signs such as dysuria, back pain and increase frequency of urination.
Prostate carcinoma is mostly adenocarcinoma. It is lined by cuboidal cells, large nuclei and nucleoli and consists of well defined gland. Prostate carcinoma may present with invasion of the lymphatic vessel and vascular vessel of prostatic capsule.
Prostate carcinoma may present with raised in prostatic acid phosphatase and raised in serum PSA. There will also be an increase in alkaline phosphatase level in case of bone metastasis.
Prostate carcinoma may spread to the bone via hematogenous spread which later lead to bony osteoblastic metastasis. Prostate carcinoma is graded based on the Gleason system of grading. Prostate carcinoma may occur as irregular, enlarged, firm nodules which is based diagnosed on by performing digital rectal examination and confirm with biopsy of the prostate gland. These nodules may arise from the peripheral zone of the posterior lobe of the prostate glands.
The treatment of prostate carcinoma may include radiotherapy, prostatectomy and anti androgen / flutamide.
