Symptom finder - The causes of polycythemia
Symptom finder - The causes of polycythemia
There are two different form of polycythemia which are known as apparent polycythemia or true polycythemia. Polycythemia is an increase in the concentration of the red cell that is accompanies with an increase in the concentration of the hemoglobin and hematocrit.
Apparent polycythemia occurs as a result of dehydration which leads to reduction in the plasma volume and normal red cell mass. The causes of apparent polycythemia are burns, dehydration and enteropathy which lead to low plasma volume and Gaisbock’s syndrome.
True polycythemia occurs as a result of increase in the mass of the red cell. True polycythemia is caused by primary polycythemia.Primary polycythemia occurs as a result of neoplasm which affect the myeloid system. Primary polycythemia is aslo known as polycythemia ruba vera. Another causes of true polycythemia is secondary polycythemia. Secondary polycythemia occurs due to cyanotic heart disease, chronic respiratory disorders, hemoglobinopathy ( high affinity), carbon monoxide exposure in smokers and hypoxia which lead to appropriate erythropoietin production.
Inappropriate erythropoietin production may also lead to true polycythemia. The common causes of inappropriate production of erythropoietin are uterine fiborids, renal carcinoma, renal cyst, cerebellar hemiangioblastoma, hapetocellular carcinoma, renal amyloidosis and renal artery stenosis.
In term of symptoms, patients are often asymptomatic. Features such as aquagenic pruritus ( which is after hot bath induced skin itching), fatigue, weight loss and sweating are commonly due to polycythemia ruba vera.
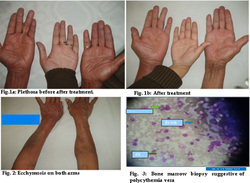
The signs of polycythemia includes facial plethora, cyanosis, splenomegaly, dilated retinal veins, engorged conjunctival vessels and scratch marks or bruising of the skin.
Always remember to observe the symptoms and signs of complication such as headache, confusion or blurred vision ( hyperviscositiy symptoms), deep vein thrombosis and stroke.
The investigation requires are full blood count, serum uric acid level, blood film, total red cell volume, bone marrow aspirates, plasma volume and arterial blood gases.
In term of full blood count, the hematocrit is usually higher than normal. The hematocrit level in women is 47% more than normal. The hematocrit level in men is 55% mote than normal. The higher the level of hematocrit the greater the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis. In this scenario, phlebotomy repeatedly is required to bring down the level of hematocrit to 45 %. Besides thrombocytosis, 50% of polycythemia vera is associated with neutrophil leucocytosis. There will also be a rise in the red cell count and hemoglobin level with 15.5 g/dl in women and 17.5 g/dl in men. Increase in the cell turnover will lead to an increase in the level of the uric acid in case of polycythemia vera. Blood film may reveal the present of myelocytes and metamyelocytes.
The red cell mass is calculated by taking red cells from a patient. The red cells are tagged with 51Cr . Later the red cells are re injected. The dilution of the 51 Cr isotopes in venous blood system are useful in determining the value of the red cell mass. In women the normal range is 22- 32 ml/kg . In men the normal ranges is 25- 35 ml/kg. The hematocrit and hemoglobin level will be normal or low and iron deficient polycythemia will occur in cases of continuous loss of blood ( peptic ulceration). It is commonly present, when there is low MCV ( iron deficient red cells) with no evidence of anemia with a red cell count which is very high in number.
There are two different form of polycythemia which are known as apparent polycythemia or true polycythemia. Polycythemia is an increase in the concentration of the red cell that is accompanies with an increase in the concentration of the hemoglobin and hematocrit.
Apparent polycythemia occurs as a result of dehydration which leads to reduction in the plasma volume and normal red cell mass. The causes of apparent polycythemia are burns, dehydration and enteropathy which lead to low plasma volume and Gaisbock’s syndrome.
True polycythemia occurs as a result of increase in the mass of the red cell. True polycythemia is caused by primary polycythemia.Primary polycythemia occurs as a result of neoplasm which affect the myeloid system. Primary polycythemia is aslo known as polycythemia ruba vera. Another causes of true polycythemia is secondary polycythemia. Secondary polycythemia occurs due to cyanotic heart disease, chronic respiratory disorders, hemoglobinopathy ( high affinity), carbon monoxide exposure in smokers and hypoxia which lead to appropriate erythropoietin production.
Inappropriate erythropoietin production may also lead to true polycythemia. The common causes of inappropriate production of erythropoietin are uterine fiborids, renal carcinoma, renal cyst, cerebellar hemiangioblastoma, hapetocellular carcinoma, renal amyloidosis and renal artery stenosis.
In term of symptoms, patients are often asymptomatic. Features such as aquagenic pruritus ( which is after hot bath induced skin itching), fatigue, weight loss and sweating are commonly due to polycythemia ruba vera.
The signs of polycythemia includes facial plethora, cyanosis, splenomegaly, dilated retinal veins, engorged conjunctival vessels and scratch marks or bruising of the skin.
Always remember to observe the symptoms and signs of complication such as headache, confusion or blurred vision ( hyperviscositiy symptoms), deep vein thrombosis and stroke.
The investigation requires are full blood count, serum uric acid level, blood film, total red cell volume, bone marrow aspirates, plasma volume and arterial blood gases.
In term of full blood count, the hematocrit is usually higher than normal. The hematocrit level in women is 47% more than normal. The hematocrit level in men is 55% mote than normal. The higher the level of hematocrit the greater the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis. In this scenario, phlebotomy repeatedly is required to bring down the level of hematocrit to 45 %. Besides thrombocytosis, 50% of polycythemia vera is associated with neutrophil leucocytosis. There will also be a rise in the red cell count and hemoglobin level with 15.5 g/dl in women and 17.5 g/dl in men. Increase in the cell turnover will lead to an increase in the level of the uric acid in case of polycythemia vera. Blood film may reveal the present of myelocytes and metamyelocytes.
The red cell mass is calculated by taking red cells from a patient. The red cells are tagged with 51Cr . Later the red cells are re injected. The dilution of the 51 Cr isotopes in venous blood system are useful in determining the value of the red cell mass. In women the normal range is 22- 32 ml/kg . In men the normal ranges is 25- 35 ml/kg. The hematocrit and hemoglobin level will be normal or low and iron deficient polycythemia will occur in cases of continuous loss of blood ( peptic ulceration). It is commonly present, when there is low MCV ( iron deficient red cells) with no evidence of anemia with a red cell count which is very high in number.
Bone marrow aspiration may reveal an increase in the deposition of reticulin and megakaryocytes. Erythroid hyperplasia and hypercellular bone marrow are common findings in polycythemia ruba vera.
Plasma volume is useful to distinguish between apparent polycythemia and real polycythemia. Low plasma volume is due to apparent polycythemia. Plasma volume and total red cell volume are measured at the same time. The normal range of plasma volume is 35- 45 ml/kg. Total plasma volume is estimated using 125I- albumin.
In arterial blood gases, the concentration of the oxygen in blood is low in secondary polycythemia as a result of right to left shunt cardiac disease and respiratory failure. In primary polycythemia the concentration of oxygen in blood is normal.
Plasma volume is useful to distinguish between apparent polycythemia and real polycythemia. Low plasma volume is due to apparent polycythemia. Plasma volume and total red cell volume are measured at the same time. The normal range of plasma volume is 35- 45 ml/kg. Total plasma volume is estimated using 125I- albumin.
In arterial blood gases, the concentration of the oxygen in blood is low in secondary polycythemia as a result of right to left shunt cardiac disease and respiratory failure. In primary polycythemia the concentration of oxygen in blood is normal.
