Symptom finder - The causes of urinary retention
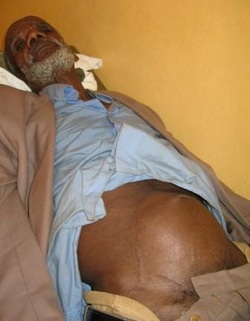
Symptom finder- The causes of urinary retention
Urinary retention is divided into acute urinary retention, chronic urinary retention and acute on chronic urinary retention.
Enlarged bladder which is painless with or without any difficulty in micturition is associated with chronic urinary retention. Painful bladder and inability to pass the urine suddenly is known as acute urinary retention. Acute urinary retention forms part of a surgical emergencies.
The causes of urinary retention are divided into generalized causes and local causes.
Generalized causes of urinary retention are intake of drugs such as alcohol, antidepressant and anticholinergic drugs. Neurological causes of generalized urinary retention are tabes dorsalis, spinal tumor, disc prolapse ( suggestive spinal cord compression and urgent opinion from neurosurgeon is required), multiple sclerosis, diabetic autonomic neuropathy and injuries to the spinal cord. Generalized causes of urinary retention is also associated with post- operative condition. Brisk hematuria may occur due to rapid emptying of the bladder after catheterization due to chronic retention.
Localized causes of urinary retention are divided into outside the wall ( pelvic tumor, fecal impaction ( common in elderly) enlargement of the prostate gland and pregnant woman), bladder wall or urethral ( urethral tumor, stricture of the urethral and urethral trauma) and a bladder neck or urethral lumen such as meatal ulcer, urethral valves, tumors, blood clot and stones.
In term of history, patient is asked regarding any injury or trauma to the spinal cord in the past. History of neurological status should be taken thoroughly. Full drug history should bee evaluated. Blood clot in the bladder is commonly associated with urological procedure. Elderly men may complain of acute urinary retention post operatively . This may occur due to drugs, prostatism, embarrassment, anxiety, pain, overload of fluid and supine posture. Patient may describe the problems of micturition such as dysuria, nocturia, hesistancy, frequency and poor stream as well as terminal dribbling and hematuria. Ureteric colic , urethritis and urinary tract infection are suggestive of the present of the stones. The stones impacted on the urethra or neck of the bladder. History of trauma such as fallen astride an object is also an important point. Urethral stricture may occur due to prolonged catheterization . The patient may be pregnant, constipated ( fecal impaction) or suffer from pelvic fracture.
Full neurological examination is considered. Look for any evidence and consequences of trauma to the spine. Guarding and pain post operative will make it hard to palpate the bladder post operatively.Assess the patient for any signs of uremia. Digital rectal examination is performed to check for any evidence of pelvic tumor or prostatic hypertrophy. High floating prostate may occur due to urethral injury as a result of trauma on digital rectal examination. Sudden onset of urinary retention is characterized by palpable , tender and painful bladder. The bladder is rarely distended above the symphysis pubis in acute urinary retention. In chronic urinary retention, the bladder is distended to the umbilicus and painless in nature. Overflow incontinence is associated with urinary retention. urethral meatus is checked for stones or ulcers. Stricture or stones is detected by palpating the course of urethra.
Urinary retention is divided into acute urinary retention, chronic urinary retention and acute on chronic urinary retention.
Enlarged bladder which is painless with or without any difficulty in micturition is associated with chronic urinary retention. Painful bladder and inability to pass the urine suddenly is known as acute urinary retention. Acute urinary retention forms part of a surgical emergencies.
The causes of urinary retention are divided into generalized causes and local causes.
Generalized causes of urinary retention are intake of drugs such as alcohol, antidepressant and anticholinergic drugs. Neurological causes of generalized urinary retention are tabes dorsalis, spinal tumor, disc prolapse ( suggestive spinal cord compression and urgent opinion from neurosurgeon is required), multiple sclerosis, diabetic autonomic neuropathy and injuries to the spinal cord. Generalized causes of urinary retention is also associated with post- operative condition. Brisk hematuria may occur due to rapid emptying of the bladder after catheterization due to chronic retention.
Localized causes of urinary retention are divided into outside the wall ( pelvic tumor, fecal impaction ( common in elderly) enlargement of the prostate gland and pregnant woman), bladder wall or urethral ( urethral tumor, stricture of the urethral and urethral trauma) and a bladder neck or urethral lumen such as meatal ulcer, urethral valves, tumors, blood clot and stones.
In term of history, patient is asked regarding any injury or trauma to the spinal cord in the past. History of neurological status should be taken thoroughly. Full drug history should bee evaluated. Blood clot in the bladder is commonly associated with urological procedure. Elderly men may complain of acute urinary retention post operatively . This may occur due to drugs, prostatism, embarrassment, anxiety, pain, overload of fluid and supine posture. Patient may describe the problems of micturition such as dysuria, nocturia, hesistancy, frequency and poor stream as well as terminal dribbling and hematuria. Ureteric colic , urethritis and urinary tract infection are suggestive of the present of the stones. The stones impacted on the urethra or neck of the bladder. History of trauma such as fallen astride an object is also an important point. Urethral stricture may occur due to prolonged catheterization . The patient may be pregnant, constipated ( fecal impaction) or suffer from pelvic fracture.
Full neurological examination is considered. Look for any evidence and consequences of trauma to the spine. Guarding and pain post operative will make it hard to palpate the bladder post operatively.Assess the patient for any signs of uremia. Digital rectal examination is performed to check for any evidence of pelvic tumor or prostatic hypertrophy. High floating prostate may occur due to urethral injury as a result of trauma on digital rectal examination. Sudden onset of urinary retention is characterized by palpable , tender and painful bladder. The bladder is rarely distended above the symphysis pubis in acute urinary retention. In chronic urinary retention, the bladder is distended to the umbilicus and painless in nature. Overflow incontinence is associated with urinary retention. urethral meatus is checked for stones or ulcers. Stricture or stones is detected by palpating the course of urethra.
Investigations require are full blood count, urea and electrolytes, ESR, mid stream urine, chest x ray, ultrasound, urodynamics, cystoscopy, PSA and urethrography.
In term of full blood count, raised white cell count is due to infection.Low Hb is associated with tumors, chronic renal failure and hematuria. Urea and electrolytes may indicates the present of obstructive uropathy and renal failure. Raised ESR is due to infection and malignancy. Mid stream urine is considered for further microscopy, culture and sensitivity studies to detect the present of urinary tract infection. Cytological studies are useful to detect any tumor. Ultrasound is considered to identify any fetus in the uterus, any dilation of the upper urinary tracy as a result of back pressure and to detect the sizes of the bladder. Chest x ray is considered to identify any tumor deposition or pulmonary edema due to chronic renal failure.
Urodynamics are considered to identify the neurological problems of the neck of the bladder. Stricture, tumor and stones are detected by using cystoscopy. Urethrography may identify any trauma to the urethra, stricture or urethral valves. Prostate carcinoma is identified by PSA.
In term of full blood count, raised white cell count is due to infection.Low Hb is associated with tumors, chronic renal failure and hematuria. Urea and electrolytes may indicates the present of obstructive uropathy and renal failure. Raised ESR is due to infection and malignancy. Mid stream urine is considered for further microscopy, culture and sensitivity studies to detect the present of urinary tract infection. Cytological studies are useful to detect any tumor. Ultrasound is considered to identify any fetus in the uterus, any dilation of the upper urinary tracy as a result of back pressure and to detect the sizes of the bladder. Chest x ray is considered to identify any tumor deposition or pulmonary edema due to chronic renal failure.
Urodynamics are considered to identify the neurological problems of the neck of the bladder. Stricture, tumor and stones are detected by using cystoscopy. Urethrography may identify any trauma to the urethra, stricture or urethral valves. Prostate carcinoma is identified by PSA.
