|
|
Pathology definition - Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
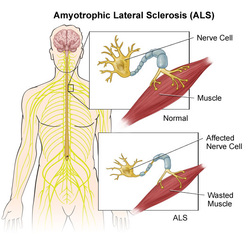
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis commonly present as a combination of upper motor neuron signs and lower motor neuron signs which affect middle age men. Upper motor neuron signs may include muscle weakness, spasticity, positive Babinski sign and hyperreflexia. Lower motor neuron signs are muscle weakness, hypotonia, hyporeflexia, atrophy of the muscle ( due to neurogenic atrophy and the presents of fiber with dark centre area on cross section/target fiber) and fasciculation.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis commonly occur as a result of loss /reduction in the number of anterior horn cell, degeneration of the corticospinal tract neuron as well as reactive gliosis.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is associated with autosomal dominant familial inheritance disorder. The common complication of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is involvement of the respiratory muscle which may lead to respiratory failure ( the common cause of death) or respiratory infection.
The treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis may include supportive therapy.
References
1.Mitchell, JD, and GD Borasio. “Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.” The Lancet 369, no. 9578 (16): 2031–2041. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60944-1.
2.Brown, Jr, Robert H., and Wim Robberecht. “Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Pathogenesis.” Seminars in Neurology 21, no. 02 (2001): 131–140. doi:10.1055/s-2001-15260.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis commonly present as a combination of upper motor neuron signs and lower motor neuron signs which affect middle age men. Upper motor neuron signs may include muscle weakness, spasticity, positive Babinski sign and hyperreflexia. Lower motor neuron signs are muscle weakness, hypotonia, hyporeflexia, atrophy of the muscle ( due to neurogenic atrophy and the presents of fiber with dark centre area on cross section/target fiber) and fasciculation.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis commonly occur as a result of loss /reduction in the number of anterior horn cell, degeneration of the corticospinal tract neuron as well as reactive gliosis.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is associated with autosomal dominant familial inheritance disorder. The common complication of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is involvement of the respiratory muscle which may lead to respiratory failure ( the common cause of death) or respiratory infection.
The treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis may include supportive therapy.
References
1.Mitchell, JD, and GD Borasio. “Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.” The Lancet 369, no. 9578 (16): 2031–2041. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60944-1.
2.Brown, Jr, Robert H., and Wim Robberecht. “Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Pathogenesis.” Seminars in Neurology 21, no. 02 (2001): 131–140. doi:10.1055/s-2001-15260.
