|
|
Pathology definition - Endocarditis
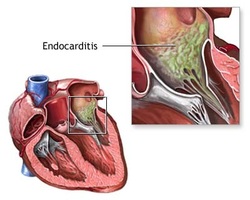
Endocarditis
There are two forms of endocarditis. Acute endocarditis and subacute endocarditis.
Acute endocarditis may present with sudden onset of murmur, fever and chills. Acute endocarditis is associated with infection by staphylococcus aureus. Acute endocarditis may present with the present of vegetation. The vegetation consists of inflammatory cells, bacteria and fibrins on aortic valve and mitral valve which are normal. The treatments of acute endocarditis are gentamicin and nafcillin.
The subacute endocarditis may present with small vegetation and fibrosis on an abnormal aortic valve and mitral valve. The vegetation consists of chronic inflammatory cells and fibrin. Subacute endocarditis may be caused by viridians streptococci. The common symptoms and signs of subacute endocarditis are insidious onset of low grade fever. Prophylaxis antibiotic ( penicillin) is considered for dental procedure in any case of subacute endocarditis.
Roth spot ( white spot which is surround with hemorrhage on the retina), splinter hemorrhage, Janeway lesion ( erythematous rash on the soles and palms) and painful nodes on digit pads( Osler node) are the common signs which are associated with acute endocarditis and subacute endocarditis.
The common complication of acute endocarditis and subacute endocarditis are septic emboli, rupture of chordae tendinae, suppurative pericarditis and valvular leaflet perforation.
References
1.MACAULAY, DUNCAN. "Acute endocarditis in infancy and early childhood." Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 88.6 (1954): 715.
2.Sande, M. A., and K. B. Courtney. "Nafcillin-gentamicin synergism in experimental staphylococcal endocarditis." The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine 88.1 (1976): 118-124.
3.Joachim, Henry, and Silik H. Polayes. "Subacute endocarditis and systemic mycosis (monilia)." Journal of the American Medical Association 115.3 (1940): 205-208.
There are two forms of endocarditis. Acute endocarditis and subacute endocarditis.
Acute endocarditis may present with sudden onset of murmur, fever and chills. Acute endocarditis is associated with infection by staphylococcus aureus. Acute endocarditis may present with the present of vegetation. The vegetation consists of inflammatory cells, bacteria and fibrins on aortic valve and mitral valve which are normal. The treatments of acute endocarditis are gentamicin and nafcillin.
The subacute endocarditis may present with small vegetation and fibrosis on an abnormal aortic valve and mitral valve. The vegetation consists of chronic inflammatory cells and fibrin. Subacute endocarditis may be caused by viridians streptococci. The common symptoms and signs of subacute endocarditis are insidious onset of low grade fever. Prophylaxis antibiotic ( penicillin) is considered for dental procedure in any case of subacute endocarditis.
Roth spot ( white spot which is surround with hemorrhage on the retina), splinter hemorrhage, Janeway lesion ( erythematous rash on the soles and palms) and painful nodes on digit pads( Osler node) are the common signs which are associated with acute endocarditis and subacute endocarditis.
The common complication of acute endocarditis and subacute endocarditis are septic emboli, rupture of chordae tendinae, suppurative pericarditis and valvular leaflet perforation.
References
1.MACAULAY, DUNCAN. "Acute endocarditis in infancy and early childhood." Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 88.6 (1954): 715.
2.Sande, M. A., and K. B. Courtney. "Nafcillin-gentamicin synergism in experimental staphylococcal endocarditis." The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine 88.1 (1976): 118-124.
3.Joachim, Henry, and Silik H. Polayes. "Subacute endocarditis and systemic mycosis (monilia)." Journal of the American Medical Association 115.3 (1940): 205-208.
