Pathology definition - Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcer disease
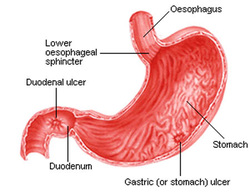
There are two form of peptic ulcer disease which include duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer.
Duodenal ulcer is associated with hyperparathyroidism, Helicobacter pylori infection, MEN type 1, smoking, young patient, chronic gastritis, Zollinger - Ellison syndrome, and blood group O individual.
Gastric ulcer commonly associate with older people, NSAIDS and Helicobacter pylori infection.
Treatment of peptic ulcer disease ( duodenal ulcer or gastric ulcer) typically focus on eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter pylori infection is usually eradicate with triple therapy such as amoxicillin or tetracycline, metronidazole and bismuth). other treatment include proton pump inhibitor and H2 receptor antagonist.
Duodenal ulcer typically present with gain in weight which is related to pain in the epigastric region if there was a decrease in the intake of meal.
Gastric ulcer typically present with weight loss which is related to epigastric pain which is greater with food/meal intake.
Duodenal ulcer may occur due to hypersecretion of the gastric acid and pepsin with a decrease in mucosal protection. There is a hypertrophy of the Brunner gland.Granulation tissue, infiltration of neutrophil an necrotic fibrinoid debris are common histological finding of duodenal ulcer. Duodenal ulcer also present with defect of the mucosal layer with punched out margin in the first part of the duodenum.
Gastric ulcer may occur due to decrease mucosal protection from the gastric acid. Gastric ulcer typically present with punched out clear margin of the mucosal defect in the pre- pyloric and antral region of the stomach.
In severe case ( duodenal ulcer or gastric ulcer) may lead to obstruction, perforation and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Laboratory investigation may reveal raise level of gastrin and decrease H+ ( hydrogen ion) secretion in gastric ulcer while increase H + (hydrogen ion) level in duodenal ulcer.
Peptic ulcer disease may also be caused by helicobacter pylori infection Helicobacter pylori is a gram negative rod with spiral sharped. Helicobacter pylori is associated with corkscrew motility.
The investigations require for detection of helicobacter pylori include urea breath test, serology testing for detection of antibody against Helicobacter pylori and gastric biopsy.
Helicobacter pylori will carries its own virulence factors. The virulence factors are polar flagella, urease, mucinase adherence factors, vacuolating cytotoxin and endotoxin. Polar flagella and mucinase facilitate the movement of the helicobacter pylori through the thick mucus layer which cover the epithelial cells of the stomach.
Urease may produce ammonia which leads to alkaline environment in the stomach. Mucin producing cells will be destroyed by the vacuolating cytotoxin. This will lead to lower production of the mucus and increase risk of ulceration due to the host inflammatory response.
Helicobacter pylori may also contributes to other forms of disorder such as gastritis or gastric adenocarcinoma.
Helicobacter pylori which inducing peptic ulcer should be treated with antibiotic , bismuth and proton pump inhibitors. The choice of antibiotics include metronidazole, tetracycline and amoxicillin.
References
1.Peek, Richard M., and M. D. Blasser. “Pathophysiology of Helicobacter Pylori-induced Gastritis and Peptic Ulcer Disease.” The American Journal of Medicine 102, no. 2 (February 1997): 200–207.
2.Hobsley, M., and P. F. Whitfield. “Pathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer.” In Ulcer and Non-Ulcer Dyspepsias, edited by Dr M. Lancaster-Smith, 1–26. Practical Clinical Medicine. Springer Netherlands, 1987.
There are two form of peptic ulcer disease which include duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer.
Duodenal ulcer is associated with hyperparathyroidism, Helicobacter pylori infection, MEN type 1, smoking, young patient, chronic gastritis, Zollinger - Ellison syndrome, and blood group O individual.
Gastric ulcer commonly associate with older people, NSAIDS and Helicobacter pylori infection.
Treatment of peptic ulcer disease ( duodenal ulcer or gastric ulcer) typically focus on eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter pylori infection is usually eradicate with triple therapy such as amoxicillin or tetracycline, metronidazole and bismuth). other treatment include proton pump inhibitor and H2 receptor antagonist.
Duodenal ulcer typically present with gain in weight which is related to pain in the epigastric region if there was a decrease in the intake of meal.
Gastric ulcer typically present with weight loss which is related to epigastric pain which is greater with food/meal intake.
Duodenal ulcer may occur due to hypersecretion of the gastric acid and pepsin with a decrease in mucosal protection. There is a hypertrophy of the Brunner gland.Granulation tissue, infiltration of neutrophil an necrotic fibrinoid debris are common histological finding of duodenal ulcer. Duodenal ulcer also present with defect of the mucosal layer with punched out margin in the first part of the duodenum.
Gastric ulcer may occur due to decrease mucosal protection from the gastric acid. Gastric ulcer typically present with punched out clear margin of the mucosal defect in the pre- pyloric and antral region of the stomach.
In severe case ( duodenal ulcer or gastric ulcer) may lead to obstruction, perforation and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Laboratory investigation may reveal raise level of gastrin and decrease H+ ( hydrogen ion) secretion in gastric ulcer while increase H + (hydrogen ion) level in duodenal ulcer.
Peptic ulcer disease may also be caused by helicobacter pylori infection Helicobacter pylori is a gram negative rod with spiral sharped. Helicobacter pylori is associated with corkscrew motility.
The investigations require for detection of helicobacter pylori include urea breath test, serology testing for detection of antibody against Helicobacter pylori and gastric biopsy.
Helicobacter pylori will carries its own virulence factors. The virulence factors are polar flagella, urease, mucinase adherence factors, vacuolating cytotoxin and endotoxin. Polar flagella and mucinase facilitate the movement of the helicobacter pylori through the thick mucus layer which cover the epithelial cells of the stomach.
Urease may produce ammonia which leads to alkaline environment in the stomach. Mucin producing cells will be destroyed by the vacuolating cytotoxin. This will lead to lower production of the mucus and increase risk of ulceration due to the host inflammatory response.
Helicobacter pylori may also contributes to other forms of disorder such as gastritis or gastric adenocarcinoma.
Helicobacter pylori which inducing peptic ulcer should be treated with antibiotic , bismuth and proton pump inhibitors. The choice of antibiotics include metronidazole, tetracycline and amoxicillin.
References
1.Peek, Richard M., and M. D. Blasser. “Pathophysiology of Helicobacter Pylori-induced Gastritis and Peptic Ulcer Disease.” The American Journal of Medicine 102, no. 2 (February 1997): 200–207.
2.Hobsley, M., and P. F. Whitfield. “Pathophysiology of Peptic Ulcer.” In Ulcer and Non-Ulcer Dyspepsias, edited by Dr M. Lancaster-Smith, 1–26. Practical Clinical Medicine. Springer Netherlands, 1987.
