Pathology definition - Turner Syndrome
Turner Syndrome
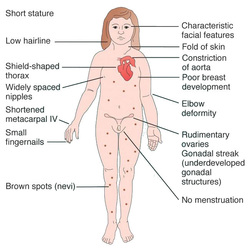
Turner syndrome may present with signs and symptoms such as webbed neck, cystic hygroma of the neck, spread nipple, broad chest, short stature and lymphedema of the extremities. Patient may also present with congenital heart defect such as coarctation of the aorta ( the common cause of short life expectancy) primary amenorrhea, infantile genitalia and fibrous strands replacement of the ovaries.
Turner syndrome may be treated with hormone therapy such as growth hormone or replacement of estrogen hormone.
Turner syndrome is caused by complete or partial monosomy of the X chromosomes and the absence of the Barr body. There will be reduction of the level of estrogen but increase in the level of LH and FSH hormone.
The common complication of Turner syndrome include increase risk of developing osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
