|
|
Pathology definition - Budd Chiari Syndrome
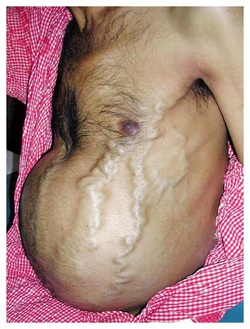
Budd Chiari Syndrome
Budd Chiari Syndrome is affecting the liver. There will be a centrilobular congestion as well as necrosis and dilation of the sinusoidal. These will finally lead to centrilobular fibrosis and formation of thrombus on the major veins.
Budd Chiari Syndrome commonly associate with hepatocellular carcinoma, pregnancy, polycythemia ruba vera, blunt trauma to the abdomen, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and the use of oral contraceptive pills.
Budd Chiari syndrome mostly occur due to hepatic vein thrombotic occlusion. Patient with Budd Chiari syndrome may present with signs and symptoms such as vomiting, jaundice, pedal edema, splenomegaly, visible vein of the abdomen and back while standing, scleral icterus and absent of jugular venous distention.
Budd Chiari Syndrome may also present with raised in liver enzyme and the present of inferior vena cava and hepatic venous thrombotic detected by doppler ultrasound.
The treatment of Budd Chiari Syndrome are restriction of salt, diuretics, ballon angioplasty, surgical bypass of obstruction and thrombolytic therapy into the hepatic vein.
References
1.Tilanus, H. W. “Budd-Chiari Syndrome.” British Journal of Surgery 82, no. 8 (1995): 1023–1030. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800820807.
2.Menon, K.V. Narayanan, Vijay Shah, and Patrick S. Kamath. “The Budd–Chiari Syndrome.” New England Journal of Medicine 350, no. 6 (2004): 578–585. doi:10.1056/NEJMra020282.
Budd Chiari Syndrome is affecting the liver. There will be a centrilobular congestion as well as necrosis and dilation of the sinusoidal. These will finally lead to centrilobular fibrosis and formation of thrombus on the major veins.
Budd Chiari Syndrome commonly associate with hepatocellular carcinoma, pregnancy, polycythemia ruba vera, blunt trauma to the abdomen, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and the use of oral contraceptive pills.
Budd Chiari syndrome mostly occur due to hepatic vein thrombotic occlusion. Patient with Budd Chiari syndrome may present with signs and symptoms such as vomiting, jaundice, pedal edema, splenomegaly, visible vein of the abdomen and back while standing, scleral icterus and absent of jugular venous distention.
Budd Chiari Syndrome may also present with raised in liver enzyme and the present of inferior vena cava and hepatic venous thrombotic detected by doppler ultrasound.
The treatment of Budd Chiari Syndrome are restriction of salt, diuretics, ballon angioplasty, surgical bypass of obstruction and thrombolytic therapy into the hepatic vein.
References
1.Tilanus, H. W. “Budd-Chiari Syndrome.” British Journal of Surgery 82, no. 8 (1995): 1023–1030. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800820807.
2.Menon, K.V. Narayanan, Vijay Shah, and Patrick S. Kamath. “The Budd–Chiari Syndrome.” New England Journal of Medicine 350, no. 6 (2004): 578–585. doi:10.1056/NEJMra020282.
