Pediatric Definition - Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis occurs due to premature closure of the cranial sutures. Craniosynostosis may lead to neurological disturbance or impair brain growth.
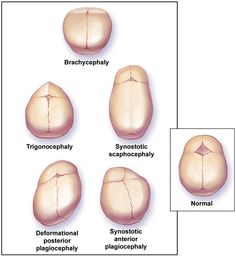
The premature closure of metopic suture may lead to metopic suture stenosis or trigonocephaly which is characterized as triangular shaped head.
The premature closure of sagittal suture may lead to scaphocephaly or dolichocephaly which is characterized as head elongation in anterior and posterior direction.
The premature closure of coronal suture may lead to brachycephaly which is characterized as increase in cranial growth from left to right.
The premature closure of lambdoid may lead to unilateral lambdoid synostosis.There will usually be one sided occipital flattening.
Craniosynostosis may also associated with hypophosphatasia or hyperthyroidism.
The treatment for craniosynostosis may include surgical correction.
Craniosynostosis occurs due to premature closure of the cranial sutures. Craniosynostosis may lead to neurological disturbance or impair brain growth.
The premature closure of metopic suture may lead to metopic suture stenosis or trigonocephaly which is characterized as triangular shaped head.
The premature closure of sagittal suture may lead to scaphocephaly or dolichocephaly which is characterized as head elongation in anterior and posterior direction.
The premature closure of coronal suture may lead to brachycephaly which is characterized as increase in cranial growth from left to right.
The premature closure of lambdoid may lead to unilateral lambdoid synostosis.There will usually be one sided occipital flattening.
Craniosynostosis may also associated with hypophosphatasia or hyperthyroidism.
The treatment for craniosynostosis may include surgical correction.