Pathology definition - Graves Disease
Graves Disease
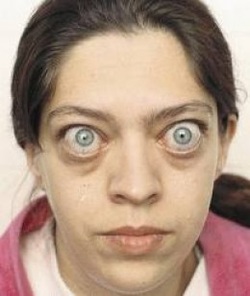
Graves disease may present with diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland. Graves disease may present with hyperthyroidism, protrusion of the eyeball ( exophthalmos ) and pretibial myxoedema.
Graves disease may present with hypercellularity with lymphocytic infiltration on the interstitium and small follicles with little colloid.
Graves disease may be treated with thyroidectomy, propylthiouracil drug/ anti thyroid drug which block the synthesis of thyroid hormone and radioactive iodine.
Graves disease is caused by the formation of the thyroid growth immunoglobulin. Thyroid growth immunoglobulin may stimulate the enlargement and hyperplasia of the thyroid gland. The other cause of Graves disease is the formation of thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin. Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin bind to thyroid follicle TSH receptors which stimulates the production of the thyroid hormone.
Graves disease is commonly affecting patient with positive HLA B8 or HLA - DR 3 and women
Graves disease may present with diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland. Graves disease may present with hyperthyroidism, protrusion of the eyeball ( exophthalmos ) and pretibial myxoedema.
Graves disease may present with hypercellularity with lymphocytic infiltration on the interstitium and small follicles with little colloid.
Graves disease may be treated with thyroidectomy, propylthiouracil drug/ anti thyroid drug which block the synthesis of thyroid hormone and radioactive iodine.
Graves disease is caused by the formation of the thyroid growth immunoglobulin. Thyroid growth immunoglobulin may stimulate the enlargement and hyperplasia of the thyroid gland. The other cause of Graves disease is the formation of thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin. Thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin bind to thyroid follicle TSH receptors which stimulates the production of the thyroid hormone.
Graves disease is commonly affecting patient with positive HLA B8 or HLA - DR 3 and women
