Pathology definition - Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
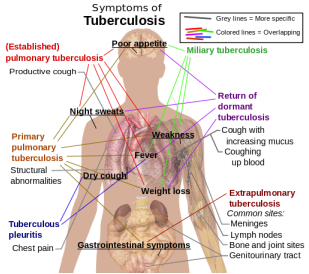
Tuberculosis is caused by inhalation of droplets which consists of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis may be asymptomatic but may also present with symptoms such as fever, weight loss, night sweat, hemoptysis and fatigue.
Tuberculosis is caused by alveolar macrophage which phagocytose the tuberculous bacilli. This will lead to a T cell mediated immune response. Tuberculosis is divided into primary tuberculosis and secondary tuberculosis.
Primary tuberculosis is a term to describe few residual bacilli who survive the action of macrophages and T cells and lay dormant in the Ghon complex. Ghon complex may present as lesion in the upper part of the lower lobe. There will be a calcified lesion with enlarged caseous hilar lymph nodes. Chest x ray may reveal calcified Ghon complex.
Reactivation of mycobacterium tuberculosis due to immunosuppression and reinfection is known as secondary tuberculosis. Secondary tuberculosis may involve the formation of the tubercle or cavitary lesion in the hilar lymph nodes or apex of the lung. Tubercle consists of caseating granuloma which consists of giant cells, fibroblasts and epithelioid cells.
Miliary tuberculosis may results in the spread of tuberculosis through the blood and lymphatic system. Tuberculosis may also involve the extrapulmonary manifestation which include Pott disease of the spine.
Investigations result such as the present of acid fast bacilli in sputum culture and positive PPD test may confirm the present of tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis is treated based on the 4 drugs regimen. The drugs include pyrazinamide,rifampicin, ethambutol, streptomycin.
Tuberculosis is caused by inhalation of droplets which consists of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis may be asymptomatic but may also present with symptoms such as fever, weight loss, night sweat, hemoptysis and fatigue.
Tuberculosis is caused by alveolar macrophage which phagocytose the tuberculous bacilli. This will lead to a T cell mediated immune response. Tuberculosis is divided into primary tuberculosis and secondary tuberculosis.
Primary tuberculosis is a term to describe few residual bacilli who survive the action of macrophages and T cells and lay dormant in the Ghon complex. Ghon complex may present as lesion in the upper part of the lower lobe. There will be a calcified lesion with enlarged caseous hilar lymph nodes. Chest x ray may reveal calcified Ghon complex.
Reactivation of mycobacterium tuberculosis due to immunosuppression and reinfection is known as secondary tuberculosis. Secondary tuberculosis may involve the formation of the tubercle or cavitary lesion in the hilar lymph nodes or apex of the lung. Tubercle consists of caseating granuloma which consists of giant cells, fibroblasts and epithelioid cells.
Miliary tuberculosis may results in the spread of tuberculosis through the blood and lymphatic system. Tuberculosis may also involve the extrapulmonary manifestation which include Pott disease of the spine.
Investigations result such as the present of acid fast bacilli in sputum culture and positive PPD test may confirm the present of tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis is treated based on the 4 drugs regimen. The drugs include pyrazinamide,rifampicin, ethambutol, streptomycin.
