Pathology definition - Amyloidosis
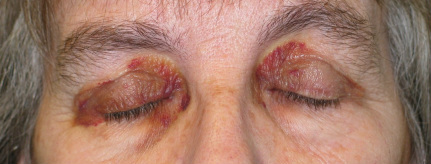
Amyloidosis
There are two forms of amyloidosis. Primary amyloidosis and secondary amyloidosis. Primary amyloidosis is associated with deposition of the AL protein or monoclonal immunoglobulin light chains. Primary amyloidosis usually affecting the tongue, kidneys, heart and muscle with strong correlation with the dyscrasias of the plasma cell.
Secondary amyloidosis is associated with deposition of the AA protein. AA protein may derived from precursors of apolipoprotein. Secondary amyloidosis mostly affecting liver, spleen, adrenal and kidneys as well as pancreas. Secondary amyloidosis may present as complication of chronic inflammation such as rheumatoid arthritis or leprosy.
There are few disorders that are associated with deposition of the amyloid such as AA protein deposit in nephropathic hereditary amyloidosis, beta microglobulin deposition in dialysis amyloidosis, calcitonin precursor derived amyloid in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, senile amyloidosis with deposition of transthyretin, diabetes with deposition of the islet amyloid polypeptide and amyloid Beta protein deposition in Alzheimer disease.
Amyloidosis may present with symptoms and signs which are related to the types of organ involved such as renal failure, nephrotic syndrome, respiratory failure, restrictive cardiomyopathy and intestinal malabsorption. The impairment of the function of the organ is associated with infiltration of insoluble protein fibrils into the tissue of the organ affected.
Histopathological studies may reveal the present of apple green birefringence of amyloid protein on Congo red stain.
There are two forms of amyloidosis. Primary amyloidosis and secondary amyloidosis. Primary amyloidosis is associated with deposition of the AL protein or monoclonal immunoglobulin light chains. Primary amyloidosis usually affecting the tongue, kidneys, heart and muscle with strong correlation with the dyscrasias of the plasma cell.
Secondary amyloidosis is associated with deposition of the AA protein. AA protein may derived from precursors of apolipoprotein. Secondary amyloidosis mostly affecting liver, spleen, adrenal and kidneys as well as pancreas. Secondary amyloidosis may present as complication of chronic inflammation such as rheumatoid arthritis or leprosy.
There are few disorders that are associated with deposition of the amyloid such as AA protein deposit in nephropathic hereditary amyloidosis, beta microglobulin deposition in dialysis amyloidosis, calcitonin precursor derived amyloid in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, senile amyloidosis with deposition of transthyretin, diabetes with deposition of the islet amyloid polypeptide and amyloid Beta protein deposition in Alzheimer disease.
Amyloidosis may present with symptoms and signs which are related to the types of organ involved such as renal failure, nephrotic syndrome, respiratory failure, restrictive cardiomyopathy and intestinal malabsorption. The impairment of the function of the organ is associated with infiltration of insoluble protein fibrils into the tissue of the organ affected.
Histopathological studies may reveal the present of apple green birefringence of amyloid protein on Congo red stain.
