Medicine Notes - Clinical Procedures - Peripheral Line Insertion
Peripheral long line insertion
Peripheral long line insertion is considered in long term treatment of patient to provide parenteral nutrition, treatment such as long term antibiotic, chemotherapy or fluid.
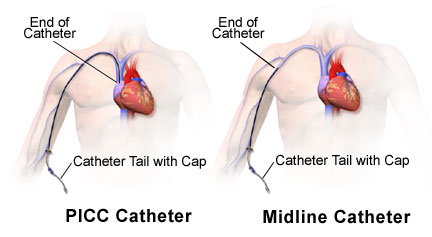
Peripheral long line can be categorized into peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs) or mid line catheters. There can be single or multilumen peripheral long lines.
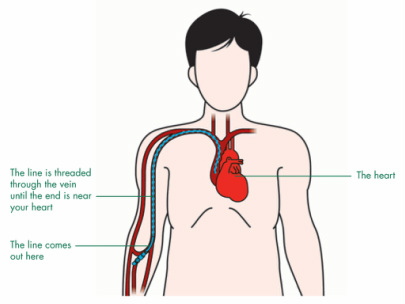
Peripheral long line is usually placed in the larger vein such as basilic vein, median cubital vein and cephalic vein. Peripheral long line is a long flexible thin catheter.
Peripherally inserted central catheter or PICCs is a long catheter approximately 60cm. The catheter can be cut into different sizes based on its suitability. This can be done by measuring the arm from the point of insertion to the clavicle and finally to the third intercostal space.
The tips of peripherally inserted central catheter or PICCs should be inserted between the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium or directly into the superior vena cava. The top should be not lower than 1-2 cm below the reflection of the pericardium or not higher than the carina. The insertion and position of the peripherally inserted central catheter or PICCs should be facilitated by the use of ultrasound. Chest radiography can also be considered.
Seldinger technique is considered in case of insertion of the peripherally inserted central catheter ( PICCs).
Midline catheter is useful for short term procedure ( less than 4 weeks) and should be avoided in drug administration ( alkaline or acidic drug). The tip of midline catheter should be ended in axillary region.
The common complication of peripheral line insertion are phlebitis / inflammation of the vein or thrombosis due to the tips present at the peripheral vascular system,bruising, bleeding, extravasation, blockage of the catheter, air embolism, infection and arrhythmias.
Peripheral long line insertion is considered in long term treatment of patient to provide parenteral nutrition, treatment such as long term antibiotic, chemotherapy or fluid.
Peripheral long line can be categorized into peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs) or mid line catheters. There can be single or multilumen peripheral long lines.
Peripheral long line is usually placed in the larger vein such as basilic vein, median cubital vein and cephalic vein. Peripheral long line is a long flexible thin catheter.
Peripherally inserted central catheter or PICCs is a long catheter approximately 60cm. The catheter can be cut into different sizes based on its suitability. This can be done by measuring the arm from the point of insertion to the clavicle and finally to the third intercostal space.
The tips of peripherally inserted central catheter or PICCs should be inserted between the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium or directly into the superior vena cava. The top should be not lower than 1-2 cm below the reflection of the pericardium or not higher than the carina. The insertion and position of the peripherally inserted central catheter or PICCs should be facilitated by the use of ultrasound. Chest radiography can also be considered.
Seldinger technique is considered in case of insertion of the peripherally inserted central catheter ( PICCs).
Midline catheter is useful for short term procedure ( less than 4 weeks) and should be avoided in drug administration ( alkaline or acidic drug). The tip of midline catheter should be ended in axillary region.
The common complication of peripheral line insertion are phlebitis / inflammation of the vein or thrombosis due to the tips present at the peripheral vascular system,bruising, bleeding, extravasation, blockage of the catheter, air embolism, infection and arrhythmias.