|
|
Pathology definition - Pemphigus Vulgaris
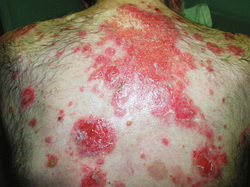
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris may present as bullae in the intraepidermal region. The bullae may rupture and lead to secondary infection. The bullae initially present on the mucosal region such as the mouth before spreading to the whole body.
Pemphigus vulgaris may present with suprabasal acantholytic blister as a result of acantholysis of the cells above the basal cell layer of the skin. Pemphigus vulgaris is associated with positive Nikolsky sign which is the present of blister after skin is rubbed with finger.
Pemphigus vulgaris is part of the autoimmune disease that involves the reaction of the IgG antibodies against the intracellular junction between the epidermal keratinocytes.
The investigations required for detection of pemphigus vulgaris may include laboratory antibodies finding and immunofluorescence studies. The investigations may reveal the present of the anti adhesion antibodies and IgG as well as complement encircling the epidermal cells,
The main treatment of pemphigus vulgaris is a series of immunosuppressive drugs as well as systemic prednisolone.
References
1.Scully, Crispian, and Stephen J. Challacombe. “Pemphigus Vulgaris: Update on Etiopathogenesis, Oral Manifestations, and Management.” Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine 13, no. 5 (September 1, 2002): 397–408. doi:10.1177/154411130201300504.
2.Becker, B A, and A A Gaspari. “Pemphigus Vulgaris and Vegetans.” Dermatologic Clinics 11, no. 3 (July 1993): 429–452.
Pemphigus vulgaris may present as bullae in the intraepidermal region. The bullae may rupture and lead to secondary infection. The bullae initially present on the mucosal region such as the mouth before spreading to the whole body.
Pemphigus vulgaris may present with suprabasal acantholytic blister as a result of acantholysis of the cells above the basal cell layer of the skin. Pemphigus vulgaris is associated with positive Nikolsky sign which is the present of blister after skin is rubbed with finger.
Pemphigus vulgaris is part of the autoimmune disease that involves the reaction of the IgG antibodies against the intracellular junction between the epidermal keratinocytes.
The investigations required for detection of pemphigus vulgaris may include laboratory antibodies finding and immunofluorescence studies. The investigations may reveal the present of the anti adhesion antibodies and IgG as well as complement encircling the epidermal cells,
The main treatment of pemphigus vulgaris is a series of immunosuppressive drugs as well as systemic prednisolone.
References
1.Scully, Crispian, and Stephen J. Challacombe. “Pemphigus Vulgaris: Update on Etiopathogenesis, Oral Manifestations, and Management.” Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & Medicine 13, no. 5 (September 1, 2002): 397–408. doi:10.1177/154411130201300504.
2.Becker, B A, and A A Gaspari. “Pemphigus Vulgaris and Vegetans.” Dermatologic Clinics 11, no. 3 (July 1993): 429–452.
